
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.

Phenylalanine is an essential α-amino acid with the formula C
9H
11NO
2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC.
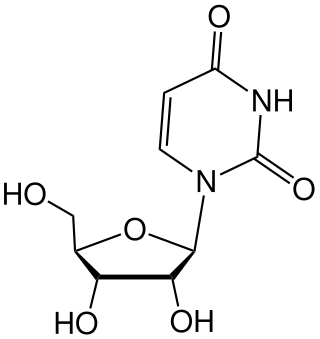
Uridine (symbol U or Urd) is a glycosylated pyrimidine analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. The analog is one of the five standard nucleosides which make up nucleic acids, the others being adenosine, thymidine, cytidine and guanosine. The five nucleosides are commonly abbreviated to their symbols, U, A, dT, C, and G, respectively. However, thymidine is more commonly written as 'dT' ('d' represents 'deoxy') as it contains a 2'-deoxyribofuranose moiety rather than the ribofuranose ring found in uridine. This is because thymidine is found in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and usually not in ribonucleic acid (RNA). Conversely, uridine is found in RNA and not DNA. The remaining three nucleosides may be found in both RNA and DNA. In RNA, they would be represented as A, C and G whereas in DNA they would be represented as dA, dC and dG.

Bupropion, formerly called amfebutamone, and sold under the brand name Wellbutrin among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, seasonal affective disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction, it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion, particularly the immediate release formulation, carries a higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants, hence caution is recommended in patients with a history of seizure disorder. The medication is taken by mouth.

The serotonin transporter also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein that transports the neurotransmitter serotonin from the synaptic cleft back to the presynaptic neuron, in a process known as serotonin reuptake.

Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Buspirone, sold under the brand name Buspar, among others, is an anxiolytic, a medication primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist, increasing action at serotonin receptors in the brain. It is taken orally, and takes two to six weeks to be fully effective.

Iproniazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was later most prominently used as an antidepressant drug. However, it was withdrawn from the market because of its hepatotoxicity. The medical use of iproniazid was discontinued in most of the world in the 1960s, but remained in use in France until its discontinuation in 2015.

Mianserin, sold under the brand name Tolvon among others, is an atypical antidepressant that is used primarily in the treatment of depression in Europe and elsewhere in the world. It is a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA). Mianserin is closely related to mirtazapine, both chemically and in terms of its actions and effects, although there are significant differences between the two drugs.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. The naturally-occurring and potent SNDRI cocaine is widely used recreationally and often illegally for the euphoric effects it produces.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

LR-5182 is a stimulant drug which acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, structurally related to the better known drug fencamfamine. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly in the 1970s, and researched for potential use as an antidepressant, although never marketed. LR-5182 has two stereoisomers, both of which are active, although one isomer blocks reuptake of only dopamine and noradrenaline, while the other blocks reuptake of serotonin as well.

Diclofensine (Ro 8-4650) was developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s in the search for a new antidepressant. It was found that the (S)-isomer was responsible for activity. Diclofensine is a stimulant drug which acts as a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor, primarily inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, with affinities (Ki) of 16.8 nM, 15.7 nM, and 51 nM for DAT, NET, and SERT (dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin transporters), respectively. It was found to be an effective antidepressant in human trials, with relatively few side effects, but was ultimately dropped from clinical development, possibly due to concerns about its abuse potential.

Amezinium metilsulfate is a sympathomimetic drug used for the treatment of low blood pressure. It has multiple mechanisms, including stimulation of alpha and beta-1 receptors and inhibition of noradrenaline and tyramine uptake.

Manifaxine is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor developed by GlaxoSmithKline through structural modification of radafaxine, an isomer of hydroxybupropion and one of the active metabolites of bupropion. Manifaxine was researched for treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obesity and was found to be safe, reasonably effective, and well-tolerated for both applications. However, no results were reported following these initial trials and development was discontinued.
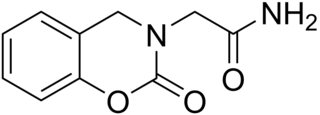
Caroxazone is an antidepressant which was formerly used for the treatment of depression but is now no longer marketed. It acts as a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (RIMA) of both MAO-A and MAO-B subtypes, with five-fold preference for the latter.

Lortalamine (LM-1404) is an antidepressant which was synthesized in the early 1980s. It acts as a potent and highly selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Lortalamine was under development for clinical use but was shelved, likely due to the finding that it produced ocular toxicity in animals. It has been used to label the norepinephrine transporter in positron emission tomography studies.

Lomevactone is a drug described as a psychostimulant and antidepressant which was synthesized and assayed in the 1980s, but was never marketed.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.

LY-2459989 is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) that has been developed by Eli Lilly as a radiotracer of that receptor, labeled either with carbon-11 or fluorine-18. It possesses high affinity for the KOR and is highly selective for it over the μ-opioid receptor and the δ-opioid receptor. LY-2459989 is a fluorine-containing analogue and follow-up compound of LY-2795050, the first KOR-selective antagonist radiotracer. Relative to LY-2795050, LY-2459989 displays 4-fold higher affinity for the KOR and similar selectivity and also possesses greatly improved central nervous system permeation. The drug appears to possess a short duration of action, with only 25% remaining in serum at 30 minutes post-injection in rhesus monkeys, making it an ideal agent for application in biomedical imaging, for instance in positron emission tomography (PET).



















