
Antipsychotics, previously known as neuroleptics and major tranquilizers, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis, principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of other psychotic disorders. They are also the mainstay, together with mood stabilizers, in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Moreover, they are also used as adjuncts in the treatment of treatment-resistant major depressive disorder.

Clozapine is a psychiatric medication and was the first atypical antipsychotic to be discovered. It is primarily used to treat people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder who have had an inadequate response to two other antipsychotics, or who have been unable to tolerate other drugs due to extrapyramidal side effects. It is also used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease.
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization M to the applied magnetic field intensity H. This allows a simple classification, into two categories, of most materials' responses to an applied magnetic field: an alignment with the magnetic field, χ > 0, called paramagnetism, or an alignment against the field, χ < 0, called diamagnetism.

Tetracyclic antidepressants (TeCAs) are a class of antidepressants that were first introduced in the 1970s. They are named after their tetracyclic chemical structure, containing four rings of atoms, and are closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), which contain three rings of atoms.
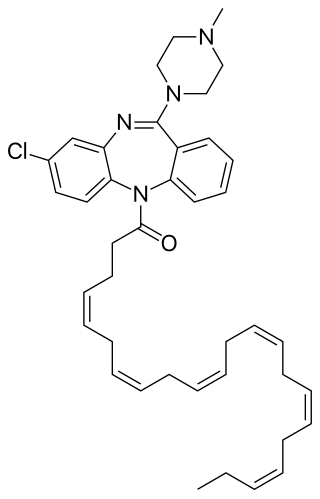
DHA-clozapine is an atypical antipsychotic drug candidate that was created and originally tested by chemists at Protarga, a small pharmaceutical in Pennsylvania, and scientists at Harvard University.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

Radafaxine (developmental code GW-353,162; also known as (2S,3S)-hydroxybupropion or (S,S)-hydroxybupropion) is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) which was under development by GlaxoSmithKline in the 2000s for a variety of different indications but was never marketed. These uses included treatment of restless legs syndrome, major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and obesity. Regulatory filing was planned for 2007, but development was discontinued in 2006 due to "poor test results".

Lasofoxifene, sold under the brand name Fablyn, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is marketed by Pfizer in Lithuania and Portugal for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and for the treatment of vaginal atrophy, and the result of an exclusive research collaboration with Ligand Pharmaceuticals (LGND). It also appears to have had a statistically significant effect of reducing breast cancer in women according to a study published in The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
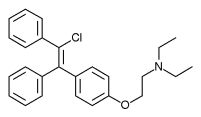
Zuclomifene (INN; or zuclomiphene (USAN)) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed. It is one of the two stereoisomers of clomifene, which itself is a mixture of 38% zuclomifene and 62% enclomifene. Zuclomifene is the (Z)-stereoisomer of clomifene, while enclomifene is the (E)-stereoisomer. Whereas zuclomifene is described as mildly estrogenic, enclomifene is described as antiestrogenic. In accordance, unlike enclomifene, zuclomifene is antigonadotropic due to activation of the estrogen receptor and reduces testosterone levels in men. It is also about five times more potent than enclomifene in inducing ovulation.

Abediterol is a once-daily experimental drug candidate for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but it has never been marketed.

Samidorphan is an opioid antagonist that in the form of olanzapine/samidorphan is used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Samidorphan reduces the weight gain associated with olanzapine. Samidorphan is taken by mouth.
Modimelanotide (INN) (code names AP-214, ABT-719, ZP-1480) is a melanocortinergic peptide drug derived from α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) which was under development by, at different times, Action Pharma, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, and Zealand for the treatment of acute kidney injury. It acts as a non-selective melanocortin receptor agonist, with IC50 values of 2.9 nM, 1.9 nM, 3.7 nM, and 110 nM at the MC1, MC3, MC4, and MC5 receptors. Modimelanotide failed clinical trials for acute kidney injury despite showing efficacy in animal models, and development was not further pursued.

AVN-101, a close structural analogue of latrepirdine, is a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist which is under development by Avineuro Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and anxiety disorders. As of November 2013, it was in phase II clinical trials for these indications.
Evenamide is a selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker, including subtypes Nav1.3, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8, which is described as an antipsychotic and is under development by Newron Pharmaceuticals as an add-on therapy for the treatment of schizophrenia. The drug has shown efficacy in animal models of psychosis, mania, depression, and aggression. It has completed phase I clinical trials, and phase II clinical trials will be commenced in the third quarter of 2015.

Brilanestrant (INN) is a nonsteroidal combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was discovered by Aragon Pharmaceuticals and was under development by Genentech for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer.

Droloxifene, also known as 3-hydroxytamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed originally in Germany and later in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer, osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women, and cardiovascular disorders but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II and phase III clinical trials for these indications before development was discontinued in 2000. The drug was found to be significantly less effective than tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer in two phase III clinical trials.

Flumezapine is an abandoned, investigational antipsychotic drug that was studied for the treatment of schizophrenia. Flumezapine failed clinical trials due to concern for liver and muscle toxicity. Flumezapine is structurally related to the common antipsychotic olanzapine—a point that was used against its manufacturer, Eli Lilly and Company, in a lawsuit in which generic manufacturers sought to void the patent on brand name olanzapine (Zyprexa). Although flumezapine does not differ greatly from olanzapine in terms of its structure, the difference was considered to be non-obvious, and Eli Lilly's patent rights on Zyprexa were upheld.

Rezvilutamide, sold under the brand name Ariane, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen which is approved for the treatment of prostate cancer in China and is or was under development for the treatment of breast cancer. It is a selective androgen receptor antagonist with reduced brain distribution compared to the structurally related nonsteroidal antiandrogen enzalutamide. The drug was developed by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine. Other structural analogues of rezvilutamide that are also used as antiandrogens besides enzalutamide include apalutamide and proxalutamide.

Serazapine (developmental code name CGS-15040A) is a serotonin 5-HT2 receptor antagonist that was investigated as a potential treatment for generalized anxiety disorder in the 1990s. In humans, serazapine was well tolerated at doses of 10 to 40 mg and was found to be superior to placebo for reducing anxiety symptoms as indicated by HAM-A scores. However, clinical development was discontinued.

Bromerguride, also known as 2-bromolisuride, is an antidopaminergic and serotonergic agent of the ergoline group which was described as having atypical antipsychotic properties but was never marketed. It was the first antidopaminergic ergoline derivative to be discovered. The pharmacodynamic actions of bromerguride are said to be "reversed" relative to its parent compound lisuride, a dopaminergic agent.

















