Muscarine, L-(+)-muscarine, or muscarin is a natural product found in certain mushrooms, particularly in Inocybe and Clitocybe species, such as the deadly C. dealbata. Mushrooms in the genera Entoloma and Mycena have also been found to contain levels of muscarine which can be dangerous if ingested. Muscarine has been found in harmless trace amounts in Boletus, Hygrocybe, Lactarius and Russula. Trace concentrations of muscarine are also found in Amanita muscaria, though the pharmacologically more relevant compound from this mushroom is the Z-drug-like alkaloid muscimol. A. muscaria fruitbodies contain a variable dose of muscarine, usually around 0.0003% fresh weight. This is very low and toxicity symptoms occur very rarely. Inocybe and Clitocybe contain muscarine concentrations up to 1.6%.

A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, also simply known as a muscarinic agonist or as a muscarinic agent, is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.

The human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M5, encoded by the CHRM5 gene, is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins. It is coupled to Gq protein. Binding of the endogenous ligand acetylcholine to the M5 receptor triggers a number of cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degradation, and potassium channel modulation. Muscarinic receptors mediate many of the effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The clinical implications of this receptor have not been fully explored; however, stimulation of this receptor is known to effectively decrease cyclic AMP levels and downregulate the activity of protein kinase A (PKA).

The adenosine A2A receptor, also known as ADORA2A, is an adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family — receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1, is a muscarinic receptor that in humans is encoded by the CHRM1 gene. It is localized to 11q13.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 2, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor that in humans is encoded by the CHRM2 gene. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. It is Gi-coupled, reducing intracellular levels of cAMP.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 4 (CHRM4), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CHRM4 gene.

The adenosine A2B receptor, also known as ADORA2B, is a G-protein coupled adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human adenosine A2b receptor gene which encodes it.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3) is an inhibitory Gi/G0-coupled G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) generally localized to presynaptic sites of neurons in classical circuits. However, in higher cortical circuits in primates, mGluR3 are localized post-synaptically, where they strengthen rather than weaken synaptic connectivity. In humans, mGluR3 is encoded by the GRM3 gene. Deficits in mGluR3 signaling have been linked to impaired cognition in humans, and to increased risk of schizophrenia, consistent with their expanding role in cortical evolution.

Xorphanol (INN), also known as xorphanol mesylate (USAN), is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that was never marketed.

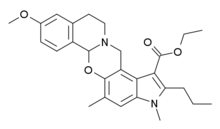
Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

UB-165 is a drug which acts as an agonist at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors being a full agonist of the α3β2 isoform and a partial agonist of the α4β2* isoform. It is used to study the role of this receptor subtype in the release of dopamine and noradrenaline in the brain, and has also been used as a lead compound to derive a number of other selective nicotinic receptor ligands.
CI-1017 is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist which is selective for and is approximately equipotent at the M1 and M4 receptors, with 20-30-fold lower affinity for the M2, M3, and M5 subtypes It is the (R)-enantiomer of the racemic compound PD-142,505.

PD-102,807 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It is used in scientific research for studying the effects of the different muscarinic receptor subtypes in the body and brain.
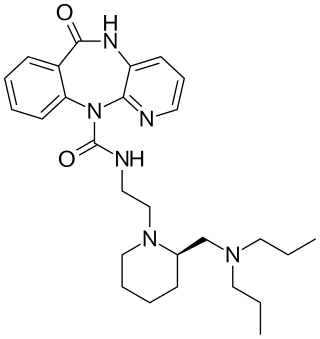
AFDX-384 (BIBN-161) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, with selectivity for the M2 and M4 subtypes. It is used mainly for mapping the distribution of M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors in the brain, and studying their involvement in the development and treatment of dementia and schizophrenia.

Tripitramine, or tripitamine, is an antimuscarinic drug which was never marketed.