
Hyoscyamine is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including henbane, mandrake, angel's trumpets, jimsonweed, the sorcerers' tree, and Atropa belladonna. It is the levorotary isomer of atropine and thus sometimes known as levo-atropine.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers. They are mainly found in the parasympathetic nervous system, but also have a role in the sympathetic nervous system in the control of sweat glands.

A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, also simply known as a muscarinic agonist or as a muscarinic agent, is an agent that activates the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor has different subtypes, labelled M1-M5, allowing for further differentiation.
Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company founded in 1992. It is headquartered in San Diego, California, and led by CEO Kevin Gorman. Neurocrine develops treatments for neurological and endocrine-related diseases and disorders. In 2017, the company's drug valbenazine (Ingrezza) was approved in the US to treat adults with tardive dyskinesia (TD).

The human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M5, encoded by the CHRM5 gene, is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins. It is coupled to Gq protein. Binding of the endogenous ligand acetylcholine to the M5 receptor triggers a number of cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degradation, and potassium channel modulation. Muscarinic receptors mediate many of the effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The clinical implications of this receptor have not been fully explored; however, stimulation of this receptor is known to effectively decrease cyclic AMP levels and downregulate the activity of protein kinase A (PKA).

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 4 (CHRM4), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CHRM4 gene.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders.

Vedaclidine (INN, codenamed LY-297,802, NNC 11-1053) is an experimental analgesic drug which acts as a mixed agonist–antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, being a potent and selective agonist for the M1 and M4 subtypes, yet an antagonist at the M2, M3 and M5 subtypes. It is orally active and an effective analgesic over 3× the potency of morphine, with side effects such as salivation and tremor only occurring at many times the effective analgesic dose. Human trials showed little potential for development of dependence or abuse, and research is continuing into possible clinical application in the treatment of neuropathic pain and cancer pain relief.

Ecopipam is a dopamine antagonist which is under development for the treatment of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Tourette syndrome, speech disorders, and restless legs syndrome. It is taken by mouth.

PD-102,807 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It is used in scientific research for studying the effects of the different muscarinic receptor subtypes in the body and brain.
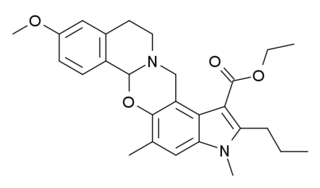
PD-0298029 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, but poor bioavailability and rapid metabolism in animal studies have meant its use is largely limited to in vitro research into the M4 and other muscarinic receptors.
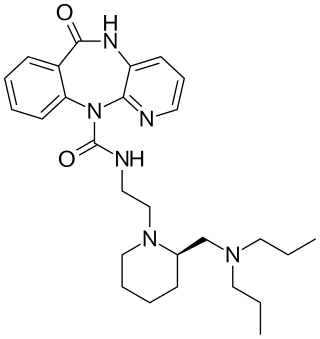
AFDX-384 (BIBN-161) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, with selectivity for the M2 and M4 subtypes. It is used mainly for mapping the distribution of M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors in the brain, and studying their involvement in the development and treatment of dementia and schizophrenia.
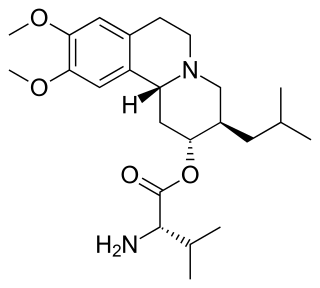
Valbenazine, sold under the brand name Ingrezza, is a medication used to treat tardive dyskinesia. It acts as a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor.

Xanomeline/trospium chloride, sold under the brand name Cobenfy, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of schizophrenia. It contains xanomeline, a muscarinic agonist; and trospium chloride, a muscarinic antagonist. Xanomeline is a functionally preferring muscarinic M4 and M1 receptor agonist. Trospium chloride is a non-selective muscarinic antagonist.
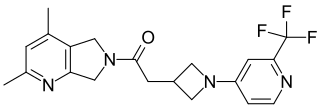
Emraclidine is an investigational antipsychotic for the treatment of both schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease psychosis developed by Cerevel Therapeutics. As of August 2024, it is in phase 2 clinical trials.
NBI-1117568 is an investigational antipsychotic drug for schizophrenia that was out-licensed Nexera Pharma in to Neurocrine Biosciences, a United States-based pharmaceutical company. It is administered orally.
NS-136 is a selective muscarinic acetylcholine M4 receptor positive allosteric modulator which is under development for the treatment of schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease. It has been found to possess pro-cognitive effects in rodents. The drug is under development by NeuShen Therapeutics. As of May 2024, it is in phase 1 clinical trials for schizophrenia and is in the preclinical stage of development for Alzheimer's disease. The drug is a small molecule, but its chemical structure does not seem to have been disclosed.
ML-007 is a selective muscarinic acetylcholine M1 and M4 receptor agonist which is under development for the treatment of schizophrenia, psychotic disorders, and dyskinesias. It is being developed in combination with a peripherally selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist (also known as ML-007/peripherally acting anticholinergic or ML-007/PAC). The drug is taken by mouth.

Itameline is a non-selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist which was under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and memory disorders but was never marketed. It has been referred to as a "nootropic".













