The European Coalition for Just and Effective Drug Policies (ENCOD), originally European NGO Council On Drugs and development is a network of European non-governmental organisations and citizens concerned with the impact of current international drug policies on the lives of the most affected sectors in Europe and the Global South. Since 1994 they have been working to advocate more just and effective drugs control policies, which include an integrated solution for all problems related to the global drugs phenomenon.
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result in unexpected side effects.

The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) is an agency of the European Union located in Lisbon, Portugal. Established in 1993, the EMCDDA strives to be the "reference point" on drug usage for the European Union's member states, and to deliver "factual, objective, reliable and comparable information" about drug usage, drug addiction and related health complications, including hepatitis, HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis.

Amfepramone, also known as diethylpropion, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes that is used as an appetite suppressant. It is used in the short-term management of obesity, along with dietary and lifestyle changes. Amfepramone is most closely chemically related to the antidepressant and smoking cessation aid bupropion, which has also been developed as a weight-loss medicine when in a combination product with naltrexone.

Ethocybin is a homologue of the mushroom alkaloid psilocybin, and a semi-synthetic psychedelic alkaloid of the tryptamine family. Effects of ethocybin are comparable to those of a shorter LSD or psilocybin trip, although intensity and duration vary depending on dosage, individual physiology, and set and setting.

This is a list of the annual prevalence of cannabis use by country as a percentage of the population aged 15–64. The indicator is an "annual prevalence" rate which is the percentage of the youth and adult population who have consumed cannabis at least once in the past survey year.

Ethcathinone, also known as ethylpropion or ETH-CAT, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone chemical classes. It is an active metabolite of the prodrug diethylcathinone and is fully responsible for its effects. Ethcathinone has been identified as an ingredient in both quasi-legal "party pills", and, along with mephedrone, has also been reported as having been sold as "ecstasy" in the Australian city of Cairns.
The drug policy of Portugal, informally called the "drug strategy", was put in place in 2000, and came into effect in July 2001. Its purpose was to reduce the number of new HIV/AIDS cases in the country, as it was estimated around half of new cases came from injection drug use.

5-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran, substituted amphetamine and substituted phenethylamine classes. 5-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury".

3,4-Dimethylmethcathinone (3,4-DMMC) is a stimulant drug first reported in 2010 as a designer drug analogue of mephedrone, apparently produced in response to the banning of mephedrone, following its widespread abuse in many countries in Europe and around the world. 3,4-DMMC has been seized as a designer drug in Australia. In vitro, 3,4-DMMC was shown to be a monoamine transporter substrate that potently inhibits norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake, and to a lesser extent dopamine reuptake.

1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane or M-ALPHA is an empathogen, reported by Alexander Shulgin in his book PIHKAL as a positional isomer of MDMA, and subsequently found being sold as a designer drug in the UK in 2010, and reported to the EMCDDA new drug monitoring service. It was described by Alexander Shulgin as similar in action to its demethylated homologue, ALPHA, but with roughly twice the duration and twice the potency.

Benzedrone (4-MBC) is a designer drug which has been found since 2010 as an ingredient in a number of "bath salt" mixes sold as recreational drugs.

RU-28306 is a tricyclic tryptamine derivative which acts as a serotonin receptor agonist, with selectivity for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 subtypes. It can be regarded either as a conformationally constrained derivative of DMT, or a structurally simplified analogue of LSD, but the binding affinity of racemic RU-28306 is closer to that of DMT, though with relatively higher affinity for 5-HT2 subtypes and lower for 5-HT1. It has been sold as a designer drug and was first reported to the EMCDDA by a forensic laboratory in Slovenia in 2017.
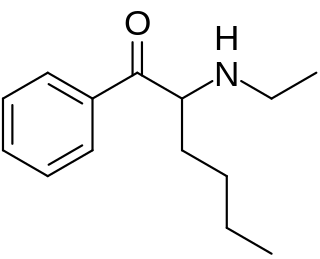
N-Ethylhexedrone (also known as α-ethylaminocaprophenone, N-ethylnorhexedrone, hexen, and NEH) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) with IC50 values of 0.0978 and 0.0467 μM, respectively. N-Ethylhexedrone was first mentioned in a series of patents by Boehringer Ingelheim in the 1960s which led to the development of the better-known drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Since the mid-2010s, N-ethylhexedrone has been sold online as a designer drug. In 2018, N-ethylhexedrone was the second most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.

Cannabis is one of the most popular controlled substances for cultivation and consumption within the country of Belgium. Following global trends, cannabis consumption rates in Belgium have been steadily increasing across the country since the 20th Century, and cannabis cultivation continues to expand rapidly on a national scale. Despite significant legal rework of cannabis-related laws since 2010, certain elements of the consumption and cultivation of cannabis are considered to exist within a “legal grey area” of Belgian law. Cannabis is technically illegal in Belgium, but personal possession has been decriminalised since 2003; adults over the age of 18 are allowed to possess up to 3 grams. The legal effort to restrict cultivation and growth has gradually subsided, resulting in an increase of the growth and consumption of cannabis and cannabis-related products.

Bromazolam (XLI-268) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) which was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified by the EMCDDA in Sweden in 2016. It is the bromo instead of chloro analogue of alprazolam and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects to it and other benzodiazepines. Bromazolam is a non subtype selective agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with a binding affinity of 2.81nM at the α1 subtype, 0.69nM at α2 and 0.62nM at α5.

α-PHiP, is a stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a positional isomer of pyrovalerone, with the methyl group shifted from the 4-position of the aromatic ring to the 4-position of the acyl chain. In a classic 2006 study of pyrrolidinyl cathinone derivatives by Meltzer et al. at Organix, the alpha-isobutyl derivative of pyrovalerone, O-2494, was found to have the highest potency in vitro as an inhibitor of the dopamine transporter of the alpha substituted derivatives tested, however it was not until ten years later in July 2016 that α-PHiP was first identified as a designer drug, when it was reported to the EMCDDA by a forensic laboratory in Slovenia.

4-EA-NBOMe is a substituted amphetamine and 25-NB derivative which has been sold as a designer drug. It was first identified by a forensic laboratory in Germany in 2014, but while its analytical properties and metabolism have been studied, its pharmacology remains unknown.
Cannabis in Tajikistan is illegal with severe penalties for the production, sale, and possession of marijuana for medicinal or recreational purposes. Punishments include up to five years in prison for possession and capital punishment or 25-year sentence for sale.

3-Methylbenzylpiperazine (3-Me-BZP) is a stimulant drug which is a derivative of benzylpiperazine. It has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in Sweden in February 2012.
















