Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over 30 kg/m2; the range 25–30 kg/m2 is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
Human body weight is a person's mass or weight.
An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. These substances work by affecting the central nervous system or certain neurotransmitters to create a feeling of fullness or reduce the desire to eat. The understanding of anorexiant effects is crucial in the development of interventions for weight management, eating disorders, and related health concerns. The anorexiant effect can be induced through diverse mechanisms, ranging from hormonal regulation to neural signaling. Ghrelin, leptin, and peptide YY are among the hormones involved in appetite control. Additionally, neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine in the central nervous system contribute significantly to the regulation of food intake.

Bromocriptine, originally marketed as Parlodel and subsequently under many brand names, is an ergoline derivative and dopamine agonist that is used in the treatment of pituitary tumors, Parkinson's disease, hyperprolactinaemia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and, as an adjunct, type 2 diabetes.
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control excess body fat. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by: reducing appetite and consequently energy intake, increasing energy expenditure, redirecting nutrients from adipose to lean tissue, or interfering with the absorption of calories.
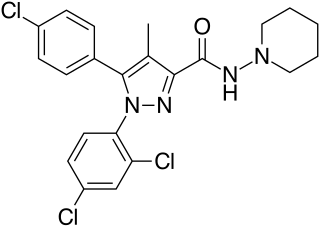
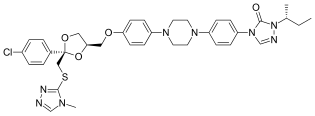
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was first-in-class for clinical development.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid, one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. It was discovered in 1940 and as of 2022, clinical research on CBD included studies related to the treatment of anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that CBD is effective for these conditions. CBD is sold as a herbal dietary supplement and promoted with yet unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects.
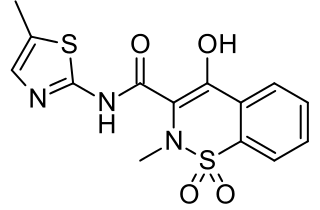
Meloxicam, sold under the brand name Mobic among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation in rheumatic diseases and osteoarthritis. It is used by mouth or by injection into a vein. It is recommended that it be used for as short a period as possible and at a low dose.

Carprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the carbazole and propionic acid class that was previously for use in humans and animals but is now only available to veterinarians for prescribing as a supportive treatment for various conditions in animals. Carprofen reduces inflammation by inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2; its specificity for COX-2 varies from species to species. Marketed under many brand names worldwide, carprofen is used as a treatment for inflammation and pain, including joint pain and postoperative pain.

Pet food is animal feed intended for consumption by pets. Typically sold in pet stores and supermarkets, it is usually specific to the type of animal, such as dog food or cat food. Most meat used for animals is a byproduct of the human food industry, and is not regarded as "human grade".

Dirlotapide is a drug used to treat obesity in dogs. It is manufactured by Pfizer and Zoetis and marketed under the brand name Slentrol.

Flupirtine is an aminopyridine that functions as a centrally acting non-opioid analgesic that was originally used as an analgesic for acute and chronic pain but in 2013 due to issues with liver toxicity, the European Medicines Agency restricted its use to acute pain, for no more than two weeks, and only for people who cannot use other painkillers. In March 2018, marketing authorisations for flupirtine were withdrawn following a European Medicines Agency recommendation based on the finding that the restrictions introduced in 2013 had not been sufficiently followed in clinical practice, and cases of serious liver injury still occurred including liver failure.

Naltrexone/bupropion, sold under the brand name Contrave among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the management of chronic obesity in adults in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It contains naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, and bupropion, an aminoketone atypical antidepressant. It is taken by mouth. Both medications have individually shown some evidence of effectiveness in weight loss, and the combination has been shown to have some synergistic effects on weight.

Obesity in pets occurs when excessive adipose tissue accumulates in the body, and is generally defined as occurring when an animal's body weight is at least 20% greater than its optimal body weight. Obesity is associated with metabolic and hormonal changes, and can predispose pets to illnesses like orthopedic disease, diabetes, and cancer.

Daratumumab, sold under the brand name Darzalex among others, is an anti-cancer monoclonal antibody medication. It binds to CD38, which is overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. Daratumumab was originally developed by Genmab, but it is now being jointly developed by Genmab along with the Johnson & Johnson subsidiary Janssen Biotech, which acquired worldwide commercialization rights to the drug from Genmab.

Fluralaner, (INN) sold under the brand name Bravecto among others, is a systemic insecticide and acaricide that is administered orally or topically. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it for flea treatment in dogs in May 2014, and approved the combination fluralaner/moxidectin as a topical treatment for cats in November 2019. The EU approved fluralaner in March 2014. Australia approved it for the treatment and prevention of ticks and fleas on dogs in January 2015. For treating mites in chickens, a solution for use in drinking water is available under the brand name Exzolt and was approved for use in the EU in 2017.
SGLT2 inhibitors are a class of medications that inhibit sodium-glucose transport proteins in the nephron, unlike SGLT1 inhibitors that perform a similar function in the intestinal mucosa. The foremost metabolic effect of this is to inhibit reabsorption of glucose in the kidney and therefore lower blood sugar. They act by inhibiting sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2). SGLT2 inhibitors are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Apart from blood sugar control, gliflozins have been shown to provide significant cardiovascular benefit in people with type 2 diabetes. As of 2014, several medications of this class had been approved or were under development. In studies on canagliflozin, a member of this class, the medication was found to enhance blood sugar control as well as reduce body weight and systolic and diastolic blood pressure.

Setmelanotide, sold under the brand name Imcivree, is a medication used for the treatment of genetic obesity caused by a rare single-gene mutation.

Semaglutide is an antidiabetic medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and an anti-obesity medication used for long-term weight management. It is a peptide similar to the hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), modified with a side chain. It can be administered by subcutaneous injection or taken orally. It is sold under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus for diabetes, and under the brand name Wegovy for weight loss.

Oclacitinib, sold under the brand name Apoquel among others, is a veterinary medication used in the control of atopic dermatitis and pruritus from allergic dermatitis in dogs at least 12 months of age. Chemically, it is a synthetic cyclohexylamino pyrrolopyrimidine janus kinase inhibitor that is relatively selective for JAK1. It inhibits signal transduction when the JAK is activated and thus helps downregulate expression of inflammatory cytokines.