Changes during circulation
Nascent VLDL released from the liver contains apolipoprotein B100, apolipoprotein C1 (apoC1), apolipoprotein E (apoE), cholesterol, cholesteryl esters, and triglycerides. As it circulates in blood, it picks up apolipoprotein C-II (apoC-II) and additional apoE donated from high-density lipoprotein (HDL). At this point, nascent VLDL becomes a mature VLDL. Once in circulation, VLDL will come in contact with lipoprotein lipase (LPL) in the capillary beds in the body (adipose, cardiac, and skeletal muscle). LPL will remove triglycerides from VLDL for storage or energy production. VLDL now meets back up with HDL where apoC-II is transferred back to HDL (but keeps apoE). HDL also transfers cholesteryl esters to the VLDL in exchange for phospholipids and triglycerides via cholesterylester transfer protein (CETP). As more and more triglycerides are removed from the VLDL because of the action of LPL and CETP enzymes, the composition of the molecule changes, and it becomes intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). [6]
Fifty percent of IDLs are recognized by receptors in the liver cells because of the apolipoprotein B-100 (apoB-100) and apoE they contain and are endocytosed. The other 50% of IDL lose apoE; when their cholesterol content becomes greater than the content of triglyceride, they become LDL, with apoB-100 as the primary apolipoprotein. The LDL is taken into a cell via the LDL receptor via endocytosis, where the contents are either stored, used for cell membrane structure, or converted into other products such as steroid hormones or bile acids. [7]
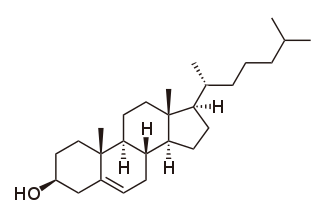
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle.

Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries.

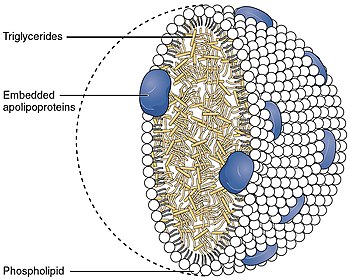
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, surrounded by a phospholipid outer shell, with the hydrophilic portions oriented outward toward the surrounding water and lipophilic portions oriented inward toward the lipid center. A special kind of protein, called apolipoprotein, is embedded in the outer shell, both stabilising the complex and giving it a functional identity that determines its role.

Chylomicra, also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. ULDLs are one of the five major groups of lipoproteins that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. A protein specific to chylomicra is ApoB48.
Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs) belong to the lipoprotein particle family and are formed from the degradation of very low-density lipoproteins as well as high-density lipoproteins. IDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. Each native IDL particle consists of protein that encircles various lipids, enabling, as a water-soluble particle, these lipids to travel in the aqueous blood environment as part of the fat transport system within the body. Their size is, in general, 25 to 35 nm in diameter, and they contain primarily a range of triglycerides and cholesterol esters. They are cleared from the plasma into the liver by receptor-mediated endocytosis, or further degraded by hepatic lipase to form LDL particles.
A lacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine.

Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-soluble enzyme that hydrolyzes triglycerides in lipoproteins, such as those found in chylomicrons and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), into two free fatty acids and one monoacylglycerol molecule:

Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph.
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally high levels of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. The term hyperlipidemia refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels.
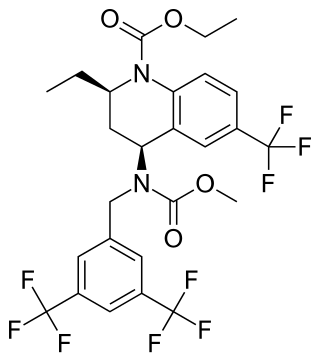
Torcetrapib was a drug being developed to treat hypercholesterolemia and prevent cardiovascular disease. Its development was halted in 2006 when phase III studies showed excessive all-cause mortality in the treatment group receiving a combination of atorvastatin (Lipitor) and torcetrapib.
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), also called plasma lipid transfer protein, is a plasma protein that facilitates the transport of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides between the lipoproteins. It collects triglycerides from very-low-density (VLDL) or Chylomicrons and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa. Most of the time, however, CETP does a heteroexchange, trading a triglyceride for a cholesteryl ester or a cholesteryl ester for a triglyceride.

Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOB gene. It is commonly used to detect risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency is a disorder of lipoprotein metabolism. The disease has two forms: Familial LCAT deficiency, in which there is complete LCAT deficiency, and Fish-eye disease, in which there is a partial deficiency.

Hepatic lipase (HL), also called hepatic triglyceride lipase (HTGL) or LIPC (for "lipase, hepatic"), is a form of lipase, catalyzing the hydrolysis of triacylglyceride. Hepatic lipase is coded by chromosome 15 and its gene is also often referred to as HTGL or LIPC. Hepatic lipase is expressed mainly in liver cells, known as hepatocytes, and endothelial cells of the liver. The hepatic lipase can either remain attached to the liver or can unbind from the liver endothelial cells and is free to enter the body's circulation system. When bound on the endothelial cells of the liver, it is often found bound to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG), keeping HL inactive and unable to bind to HDL (high-density lipoprotein) or IDL (intermediate-density lipoprotein). When it is free in the bloodstream, however, it is found associated with HDL to maintain it inactive. This is because the triacylglycerides in HDL serve as a substrate, but the lipoprotein contains proteins around the triacylglycerides that can prevent the triacylglycerides from being broken down by HL.
Blood lipids are lipids in the blood, either free or bound to other molecules. They are mostly transported in a phospholipid capsule, and the type of protein embedded in this outer shell determines the fate of the particle and its influence on metabolism. Examples of these lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides. The concentration of blood lipids depends on intake and excretion from the intestine, and uptake and secretion from cells. Hyperlipidemia is the presence of elevated or abnormal levels of lipids and/or lipoproteins in the blood, and is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.

Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia or type III hyperlipoproteinemia is a condition characterized by increased total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and decreased HDL levels.
Reverse cholesterol transport is a multi-step process resulting in the net movement of cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to the liver first via entering the lymphatic system, then the bloodstream.

Evacetrapib was a drug under development by Eli Lilly & Company that inhibits cholesterylester transfer protein. CETP collects triglycerides from very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) or low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa, but primarily increasing high-density lipoprotein and lowering low-density lipoprotein. It is thought that modifying lipoprotein levels modifies the risk of cardiovascular disease. The first CETP inhibitor, torcetrapib, was unsuccessful because it increased levels of the hormone aldosterone and increased blood pressure, which led to excess cardiac events when it was studied. Evacetrapib does not have the same effect. When studied in a small clinical trial in people with elevated LDL and low HDL, significant improvements were noted in their lipid profile.
The vertical auto profile (VAP) test is a cholesterol, lipid and lipoprotein test.