The ATP-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA12 gene.

Sitosterolemia is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder. It is characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols. Healthy persons absorb only about 5% of dietary plant sterols, but sitosterolemia patients absorb 15% to 60% of ingested sitosterol without excreting much into the bile. The phytosterol campesterol is more readily absorbed than sitosterol.
ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes encode for two proteins sterolin-1 and -2, respectively. Sterolin-1 and –2 are two ‘half’ adenosine triphosphate binding (ATP) cassette (ABC) transporters which found to be indispensable for the regulation of sterol absorption and excretion. Mutations in either genes result in a lipid disorder, sitosterolemia.

Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly. Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH. Nevertheless, treatment is usually effective.

The ATP-binding cassette 4 gene encodes the Multidrug resistance protein 3. ABCB4 is associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.

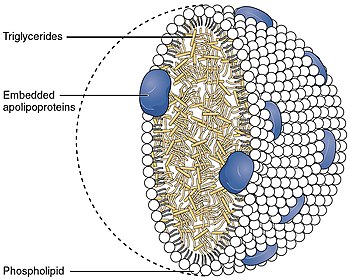
ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCA1, also known as the cholesterol efflux regulatory protein (CERP) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCA1 gene. This transporter is a major regulator of cellular cholesterol and phospholipid homeostasis.

ATP-binding cassette super-family G member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG2 gene. ABCG2 has also been designated as CDw338. ABCG2 is a translocation protein used to actively pump drugs and other compounds against their concentration gradient using the bonding and hydrolysis of ATP as the energy source.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG1 gene. It is a homolog of the well-known Drosophila gene white.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG8 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA2 gene.

Ileal sodium/bile acid cotransporter, also known as apical sodium–bile acid transporter (ASBT) and ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT), is a bile acid:sodium symporter protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC10A2 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA7 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA3 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 7, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB7 gene.

Zinc finger protein 202 is a transcription factor first associated with breast cancer. It is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ZNF202 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD4 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG4 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA8 gene.

ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA5 gene.