
Alagille syndrome (ALGS) is a genetic disorder that affects primarily the liver and the heart. Problems associated with the disorder generally become evident in infancy or early childhood. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and the estimated prevalence of Alagille syndrome is 1 in every 30,000 to 1 in every 40,000 live births. It is named after the French pediatrician Daniel Alagille, who first described the condition in 1969.
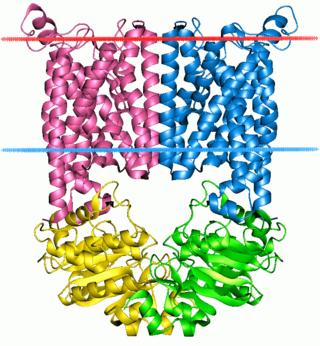
The ATP-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases.

P-glycoprotein 1 also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein of the cell membrane that pumps many foreign substances out of cells. More formally, it is an ATP-dependent efflux pump with broad substrate specificity. It exists in animals, fungi, and bacteria, and it likely evolved as a defense mechanism against harmful substances.

Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic.
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of familial cholestatic conditions caused by defects in biliary epithelial transporters. The clinical presentation usually occurs first in childhood with progressive cholestasis. This usually leads to failure to thrive, cirrhosis, and the need for liver transplantation.
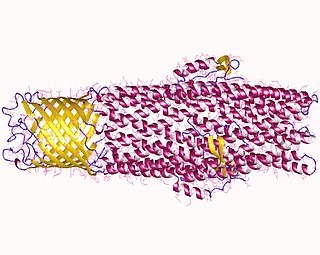
In microbiology, efflux is the moving of a variety of different compounds out of cells, such as antibiotics, heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that encode efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species - the most concerning being antibiotic resistance because microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media.

Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), also known as obstetric cholestasis, cholestasis of pregnancy, jaundice of pregnancy, and prurigo gravidarum, is a medical condition in which cholestasis occurs during pregnancy. It typically presents with itching and can lead to complications for both mother and fetus.

ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B member 11 also known as ABCB11 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCB11 gene.

Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP8B1 gene. This protein is associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 as well as benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC1 gene.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) also called canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1 (cMOAT) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 (ABCC2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC2 gene.
Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC3 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA3 gene.

ATP-binding cassette super-family B member 6, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB6 gene.

Choline kinase beta (CK), also known as Ethanolamine kinase (EK), Choline kinase-like protein , choline/ethanolamine kinase beta (CKEKB), or Choline/ethanolamine kinase is a protein encoded by the CHKB gene. This gene is found on chromosome 22 in humans. The encoded protein plays a key role in phospholipid biosynthesis. Choline kinase (CK) and ethanolamine kinase (EK) catalyzes the first step in phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis. Read-through transcripts are expressed from this locus that include exons from the downstream CPT1B locus.

Solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLCO1A2 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 8, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB8 gene.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC12 gene.
Antineoplastic resistance, often used interchangeably with chemotherapy resistance, is the resistance of neoplastic (cancerous) cells, or the ability of cancer cells to survive and grow despite anti-cancer therapies. In some cases, cancers can evolve resistance to multiple drugs, called multiple drug resistance.



















