 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a682711 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.498 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
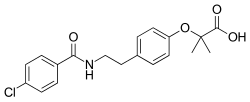
| Formula | C19H20ClNO4 |
| Molar mass | 361.82 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bezafibrate (marketed as Bezalip and various other brand names) is a fibrate drug used as a lipid-lowering agent to treat hyperlipidaemia. It helps to lower LDL cholesterol and triglyceride in the blood, and increase HDL.
Contents
It was patented in 1971 and approved for medical use in 1978. [1]
