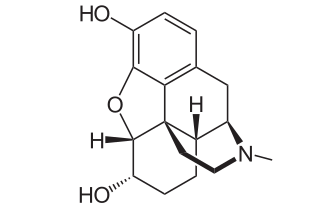
Dihydromorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid structurally related to and derived from morphine. The 7,8-double bond in morphine is reduced to a single bond to get dihydromorphine. Dihydromorphine is a moderately strong analgesic and is used clinically in the treatment of pain and also is an active metabolite of the analgesic opioid drug dihydrocodeine. Dihydromorphine occurs in trace quantities in assays of opium on occasion, as does dihydrocodeine, dihydrothebaine, tetrahydrothebaine, etc. The process for manufacturing dihydromorphine from morphine for pharmaceutical use was developed in Germany in the late 19th century, with the synthesis being published in 1900 and the drug introduced clinically as Paramorfan shortly thereafter. A high-yield synthesis from tetrahydrothebaine was later developed.

Levomethorphan (LVM) (INN, BAN) is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that has never been marketed. It is the L-stereoisomer of racemethorphan (methorphan). The effects of the two isomers of racemethorphan are quite different, with dextromethorphan (DXM) being an antitussive at low doses and a dissociative hallucinogen at much higher doses. Levomethorphan is about five times stronger than morphine.

Properidine is an opioid, an analgesic, and the isopropyl analog of pethidine. Properidine is under international control and is listed in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act (1970) as a Schedule I substance. It is a narcotic, with an Administrative Controlled Substances Code Number (ACSCN) of 9644 and a 2 gramme annual aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The salt in use is hydrochloride, with a free base conversion ratio of 0.88.

Metopon is an opioid analogue that is a methylated derivative of hydromorphone which was invented in 1929 as an analgesic.

Hydroxypethidine (Bemidone) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the more commonly used pethidine (meperidine). Hydroxypethidine is slightly more potent than meperidine as an analgesic, 1.5x meperidine in potency, and it also has NMDA antagonist properties like its close relative ketobemidone.

Normethadone, also known as desmethylmethadone or phenyldimazone, is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive agent. Normethadone is listed under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961 and is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance in the United States, with a DEA ACSCN of 9635 and an annual manufacturing quota of 2 grams. It has an effective span of action for about 14 days, and is 12 to 20 times stronger than morphine. The salts in use are the hydrobromide, hydrochloride (0.890), methyliodide (0.675), oxalate (0.766), picrate (0.563), and the 2,6-ditertbutylnapthalindisulphonate (0.480).
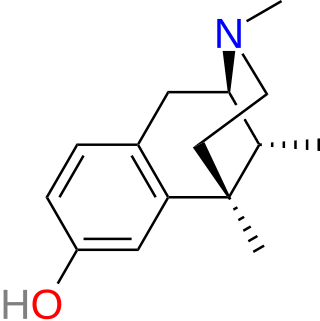
Metazocine is an opioid analgesic related to pentazocine. While metazocine has significant analgesic effects, mediated through a mixed agonist–antagonist action at the mu opioid receptor, its clinical use is limited by dysphoric and hallucinogenic effects which are most likely caused by activity at kappa opioid receptors and/or sigma receptors.

Allylprodine is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of prodine. It was discovered by Hoffman-La Roche in 1957 during research into the related drug pethidine. Derivatives were tested to prove the theory that phenolic and non-phenolic opioids bind at different sites of the opiate receptor.
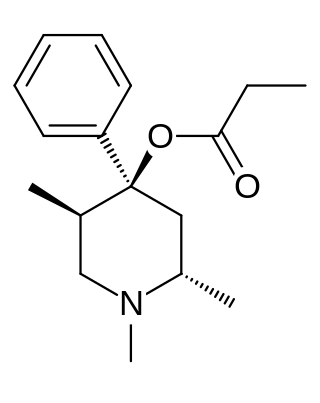
Trimeperidine is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.

Phenazocine is an opioid analgesic drug, which is related to pentazocine and has a similar profile of effects.

Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid Co. Although never given a general release, it was research found that 60 mg of phenampromide is equivalent to about 50 mg of codeine. Tests on its two enantiomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S)-isomer. Introduction of a phenyl group to the 4-position of the piperidine-ring produces a drug 60-fold more potent than morphine. The most potent reported derivative is 4-hydroxy-4-phenyl phenapromide which displays analgesic activity some x150 greater than morphine.

Ethoheptazine is an opioid analgesic from the phenazepane family. It was invented in the 1950s and is a ring expanded analogue of pethidine.

Norpethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is both a precursor to, and the toxic metabolite of, pethidine (meperidine). It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9233. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 11 grams (0.39 oz).

Benzethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine.
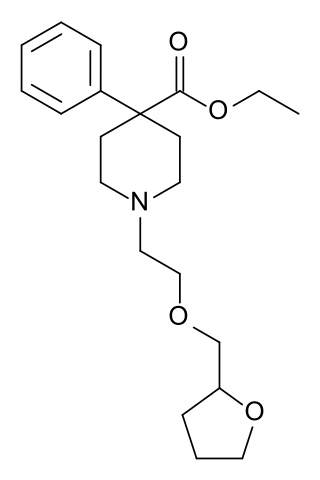
Furethidine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine), but with around 25x higher potency. According to another source, Furethidine is 500/30 = 16.7 x the potency of pethidine.

Pethidine intermediate A is a four-phenylpiperidine derivative that is a precursor to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine). It is not known to have any analgesic activity in its own right, however other derivatives of pethidine with a 4-cyano group in place of the carboxylate ethyl ester have been found to be active, so pethidine intermediate A might also show opioid effects. It is scheduled by UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. It is a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the United States and has an ACSCN of 9232. The 2014 annual manufacturing quota was 6 grammes.
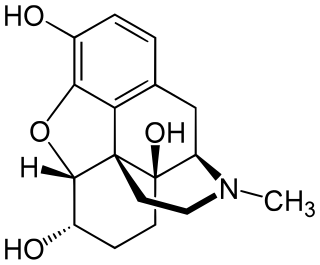
Hydromorphinol, is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 14-position has been hydroxylated and the 7,8- double bond saturated. It has similar effects to morphine such as sedation, analgesia and respiratory depression, but is twice as potent as morphine and has a steeper dose-response curve and longer half-life. It is used in medicine as the bitartrate salt and hydrochloride

Methyldesorphine is an opioid analgesic. First synthesized in Germany in 1940 and patented in the US in 1952, it has a high potential for abuse as with any potent opioid agonist, and is sometimes found along with desomorphine as a component of the home-made opioid mixture known as "Krokodil" used in Russia and the neighboring former Soviet republics. It is approximately 15 times more potent than morphine as an analgesic but if the 6-7 bond is saturated, the β isomer is some 50 times more potent than morphine.

Racemoramide, or simply moramide, is an opioid analgesic and a racemic mixture of the substances dextromoramide and levomoramide, two enantiomers of a chiral molecule.

Isomethadone (INN, BAN; trade name Liden; also known as isoamidone) is a synthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive related to methadone that was used formerly as a pharmaceutical drug but is now no longer marketed. Isomethadone was used as both an analgesic and antitussive. It binds to and activates both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with the (S)-isomer being the more potent of the two enantiomers. Isomethadone is a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States, with an ACSCN of 9226 and a 2014 aggregate manufacturing quota of 5 g. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (HBr, free base conversion ratio 0.793), hydrochloride (HCl, 0.894), and HCl monohydrate (0.850). Isomethadone is also regulated internationally as a Schedule I controlled substance under the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961.




















