
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires, but may also be used for pest control (fumigation), communication, defensive and offensive capabilities in the military, cooking, or smoking. It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.

Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics and pesticides, explosives and drugs. It has also been used to make bile acids, cholesterol and steroids.

A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires.

Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP or B[a]P) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the result of incomplete combustion of organic matter at temperatures between 300 °C (572 °F) and 600 °C (1,112 °F). The ubiquitous compound can be found in coal tar, tobacco smoke and many foods, especially grilled meats. The substance with the formula C20H12 is one of the benzopyrenes, formed by a benzene ring fused to pyrene. Its diol epoxide metabolites (more commonly known as BPDE) react with and bind to DNA, resulting in mutations and eventually cancer. It is listed as a Group 1 carcinogen by the IARC. In the 18th century a scrotal cancer of chimney sweepers, the chimney sweeps' carcinoma, was already known to be connected to soot.

Methylcholanthrene is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures. Methylcholanthrene is also known as 3-methylcholanthrene, 20-methylcholanthrene or the IUPAC name 3-methyl-1,2-dyhydrobenzo[j]aceanthrylene. The short notation often used is 3-MC or MCA. This compound forms pale yellow solid crystals when crystallized from benzene and ether. It has a melting point around 180 °C and its boiling point is around 280 °C at a pressure of 80 mmHg. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz[a]anthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.

Triphenylene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)3. A flat polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), it consists of four fused benzene rings. Triphenylene has delocalized 18-π-electron systems based on a planar structure, corresponding to the symmetry group D3h. It is a white or colorless solid.

Tetracene, also called naphthacene, is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. It has the appearance of a pale orange powder. Tetracene is the four-ringed member of the series of acenes. Tetracene is a molecular organic semiconductor, used in organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). In May 2007, researchers from two Japanese universities, Tohoku University in Sendai and Osaka University, reported an ambipolar light-emitting transistor made of a single tetracene crystal. Ambipolar means that the electric charge is transported by both positively charged holes and negatively charged electrons. Tetracene can be also used as a gain medium in dye lasers as a sensitiser in chemoluminescence.
In the field of organic chemistry, a polycyclic compound is an organic compound featuring several closed rings of atoms, primarily carbon. These ring substructures include cycloalkanes, aromatics, and other ring types. They come in sizes of three atoms and upward, and in combinations of linkages that include tethering, fusing, links via a single atom, bridged compounds, and longifolene. Though poly- literally means "many", there is some latitude in determining how many rings are required to be considered polycyclic; many smaller rings are described by specific prefixes, and so while it can refer to these, the title term is used with most specificity when these alternative names and prefixes are unavailable.

Chrysene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with the molecular formula C
18H
12 that consists of four fused benzene rings. It is a natural constituent of coal tar, from which it was first isolated and characterized. It is also found in creosote at levels of 0.5–6 mg/kg.
In organic and physical organic chemistry, Clar's rule is an empirical rule that relates the chemical stability of a molecule with its aromaticity. It was introduced in 1972 by the Austrian organic chemist Erich Clar in his book The Aromatic Sextet. The rule states that given a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the resonance structure most important to characterize its properties is that with the largest number of aromatic π-sextets i.e. benzene-like moieties.
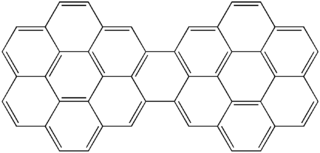
Dicoronylene is the trivial name for a very large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Its formal name is benzo[10,11]phenanthro[2',3',4',5',6':4,5,6,7]chryseno[1,2,3-bc]coronene or benzo[1,2,3-bc:4,5,6-b'c']dicoronene. It has 15 rings and is a brick-red solid. Its formula is C
48H
20. Dicoronylene sublimes under high vacuum, 0.001 torr, between 250 °C and 300 °C.

A benzopyrene is an organic compound with the formula C20H12. Structurally speaking, the colorless isomers of benzopyrene are pentacyclic hydrocarbons and are fusion products of pyrene and a phenylene group. Two isomeric species of benzopyrene are benzo[a]pyrene and the less common benzo[e]pyrene. They belong to the chemical class of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

Benzo[j]fluoranthene (BjF) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H12. Classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), it is a colourless solid that is poorly soluble in most solvents. Impure samples can appear off white. Closely related isomeric compounds include benzo[a]fluoranthene (BaF), bendo[b]fluoranthene (BbF), benzo[e]fluoranthene (BeF), and benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF). BjF is present in fossil fuels and is released during incomplete combustion of organic matter. It has been traced in the smoke of cigarettes, exhaust from gasoline engines, emissions from the combustion of various types of coal and emissions from oil heating, as well as an impurity in some oils such as soybean oil.

9,10-Dihydroanthracene is an organic compound that is derived from the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon anthracene. Several isomers of dihydroanthracene are known, but the 9,10 derivative is most common. It is a colourless solid that is used as a carrier of H2 as a hydrogen-donor.

Benz[e]acephenanthrylene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H12. It is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) made of four benzene rings around a 5-membered ring.

Dibenzopyrenes are a group of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with the molecular formula C24H14. There are five isomers of dibenzopyrene which differ by the arrangement of aromatic rings: dibenzo[a,e]pyrene, dibenzo[a,h]pyrene, dibenzo[a,i]pyrene, dibenzo[a,l]pyrene, and dibenzo[e,l]pyrene.
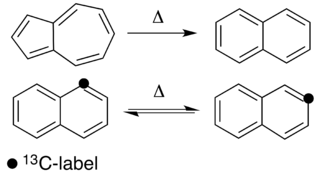
Thermal rearrangements of aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to be unimolecular reactions that directly involve the atoms of an aromatic ring structure and require no other reagent than heat. These reactions can be categorized in two major types: one that involves a complete and permanent skeletal reorganization (isomerization), and one in which the atoms are scrambled but no net change in the aromatic ring occurs (automerization). The general reaction schemes of the two types are illustrated in Figure 1.
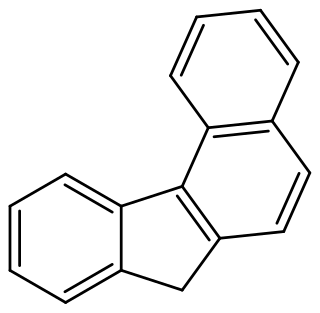
Benzo[c]fluorene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with mutagenic activity. It is a component of coal tar, cigarette smoke and smog and thought to be a major contributor to its carcinogenic properties. The mutagenicity of benzo[c]fluorene is mainly attributed to formation of metabolites that are reactive and capable of forming DNA adducts. According to the KEGG it is a group 3 carcinogen. Other names for benzo[c]fluorene are 7H-benzo[c]fluorene, 3,4-benzofluorene, and NSC 89264.
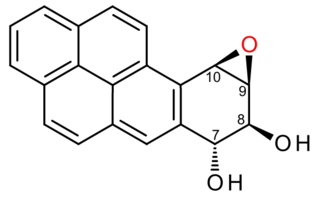
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is an organic compound with molecular formula C20H14O3. It is a metabolite and derivative of benzo[a]pyrene (found in tobacco smoke) as a result of oxidation to include hydroxyl and epoxide functionalities. (+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide binds to the N2 atom of a guanine nucleobase in DNA, distorting the double helix structure by intercalation of the pyrene moiety between base pairs through π-stacking. The carcinogenic properties of tobacco smoking are attributed in part to this compound binding and inactivating the tumor suppression ability of certain genes, leading to genetic mutations and potentially to cancer.



















