
Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP or B[a]P) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the result of incomplete combustion of organic matter at temperatures between 300 °C (572 °F) and 600 °C (1,112 °F). The ubiquitous compound can be found in coal tar, tobacco smoke and many foods, especially grilled meats. The substance with the formula C20H12 is one of the benzopyrenes, formed by a benzene ring fused to pyrene. Its diol epoxide metabolites (more commonly known as BPDE) react with and bind to DNA, resulting in mutations and eventually cancer. It is listed as a Group 1 carcinogen by the IARC. In the 18th century a scrotal cancer of chimney sweepers, the chimney sweeps' carcinoma, was already known to be connected to soot.
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 2B: The agent (mixture) is "possibly carcinogenic to humans". The exposure circumstance entails exposures that are possibly carcinogenic to humans. This category is used for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans and less than sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. It may also be used when there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some instances, an agent, mixture or exposure circumstance for which there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but limited evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals together with supporting evidence from other relevant data may be placed in this group. Further details can be found in the preamble to the IARC Monographs.
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 3: The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. This category is used most commonly for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans and inadequate or limited in experimental animals. Exceptionally, agents (mixtures) for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans but sufficient in experimental animals may be placed in this category when there is strong evidence that the mechanism of carcinogenicity in experimental animals does not operate in humans. Agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances that do not fall into any other group are also placed in this category.

Fluoranthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). The molecule can be viewed as the fusion of naphthalene and benzene unit connected by a five-membered ring. Although samples are often pale yellow, the compound is colorless. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is a member of the class of PAHs known as non-alternant PAHs because it has rings other than those with six carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of the alternant PAH pyrene. It is not as thermodynamically stable as pyrene. Its name is derived from its fluorescence under UV light.
Mycobacterium pyrenivorans is a scotochromogenic, rapidly growing mycobacterium, first isolated from an enrichment culture obtained from soil that was highly contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The soil sample was collected on the site of a former coking plant at Ubach-Palenberg, Germany. Etymology: pyrenivorans; digesting pyrene.
The Water Supply Water Quality Regulations 1989 are regulations imposed on the England and Wales Water industry by Statutory Instrument. The regulations were signed jointly by Peter Walker, Secretary of State for Wales and Michael Howard who, as Minister for Water and Planning, was responsible for implementing water privatization in England and Wales during 1988/89.
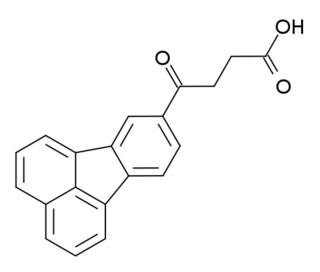
Florantyrone is a drug used in the treatment of biliary dyskinesia. It is also known as a cholagogue and choleretic.

A benzopyrene is an organic compound with the formula C20H12. Structurally speaking, the colorless isomers of benzopyrene are pentacyclic hydrocarbons and are fusion products of pyrene and a phenylene group. Two isomeric species of benzopyrene are benzo[a]pyrene and the less common benzo[e]pyrene. They belong to the chemical class of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
The molecular formula C20H12 may refer to:

Dibenzothiepins are chemical compounds which are derivatives of thiepin with two benzene rings.
Benzo[c]phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C18H12. It is a white solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is a nonplanar molecule consisting of the fusion of four fused benzene rings. The compound is of mainly theoretical interest but it is environmentally occurring and weakly carcinogenic.

Benzo[ghi]perylene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C22H12.

Benzo[j]fluoranthene (BjF) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H12. Classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), it is a colourless solid that is poorly soluble in most solvents. Impure samples can appear off white. Closely related isomeric compounds include benzo[a]fluoranthene (BaF), bendo[b]fluoranthene (BbF), benzo[e]fluoranthene (BeF), and benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF). BjF is present in fossil fuels and is released during incomplete combustion of organic matter. It has been traced in the smoke of cigarettes, exhaust from gasoline engines, emissions from the combustion of various types of coal and emissions from oil heating, as well as an impurity in some oils such as soybean oil.
Benzofluoranthene may refer to:
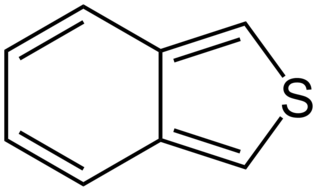
Benzo[c]thiophene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H6S.

Methysticin is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant. Research suggests that methysticin and the related compound dihydromethysticin have CYP1A1 inducing effects which may be responsible for their toxicity. Additionally, methysticin has been shown to potentiate GABAA receptor activity, contributing to the overall anxiolytic profile of the kava plant.

Benzo[a]fluoranthene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H12.

Altechromone A is a chromone derivative. To date, it has been isolated from plant families such as Polygonaceae, Lamiaceae, Fabaceae, and Hypericaceae.
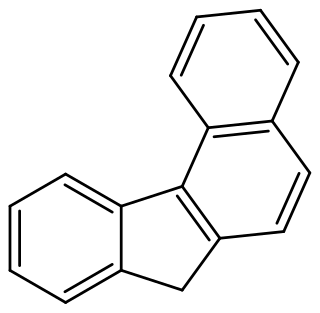
Benzo[c]fluorene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with mutagenic activity. It is a component of coal tar, cigarette smoke and smog and thought to be a major contributor to its carcinogenic properties. The mutagenicity of benzo[c]fluorene is mainly attributed to formation of metabolites that are reactive and capable of forming DNA adducts. According to the KEGG it is a group 3 carcinogen. Other names for benzo[c]fluorene are 7H-benzo[c]fluorene, 3,4-benzofluorene, and NSC 89264.

Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), one of 16 PAHs generally measured in studies of environmental exposure and air pollution. Many compounds of this class are formed when burning coal, oil, gas, wood, household waste and tobacco, and can bind to or form small particles in the air. The compounds are known to have toxic, mutagenic and/or carcinogenic properties. Over 100 different PAHs have been identified in environmental samples. One of these 16 is Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene (IP). IP is the combination of an indeno molecule and a pyrene molecule with a fluoranthene network. In 1962, the National Cancer Institute reported that indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene has a slight tumor activity. This was confirmed in 1973 by the IARC in mice testing.













