
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin, is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane, where n = 1, to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane.
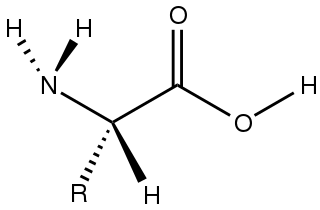
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life.

An alpha helix is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil.

Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.
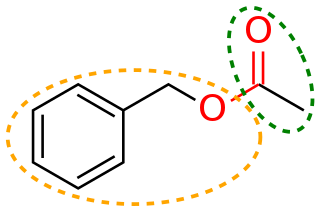
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.
A monomer is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.

Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences.
In polymer science, the polymer chain or simply backbone of a polymer is the main chain of a polymer. Polymers are often classified according to the elements in the main chains. The character of the backbone, i.e. its flexibility, determines the properties of the polymer. For example, in polysiloxanes (silicone), the backbone chain is very flexible, which results in a very low glass transition temperature of −123 °C. The polymers with rigid backbones are prone to crystallization in thin films and in solution. Crystallization in its turn affects the optical properties of the polymers, its optical band gap and electronic levels.

A biomolecule or biological molecule is loosely defined as a molecule produced by a living organism and essential to one or more typically biological processes. Biomolecules include large macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as vitamins and hormones. A general name for this class of material is biological materials. Biomolecules are an important element of living organisms. They are often endogenous, i.e. produced within the organism, but organisms usually also need exogenous biomolecules, for example certain nutrients, to survive.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers. The name is composed of Greek elements oligo-, "a few" and -mer, "parts". An adjective form is oligomeric.
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.

The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and to be excluded by water. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar substances, which maximizes the entropy of water and minimizes the area of contact between water and nonpolar molecules. In terms of thermodynamics, the hydrophobic effect is the free energy change of water surrounding a solute. A positive free energy change of the surrounding solvent indicates hydrophobicity, whereas a negative free energy change implies hydrophilicity.
In the nomenclature of organic chemistry, a locant is a term to indicate the position of a functional group or substituent within a molecule.
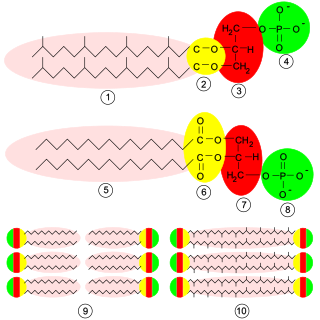
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes in eukaryotic cells. They are a type of lipid, of which its composition affects membrane structure and properties. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.
In polymer chemistry, branching is the regular or irregular attachment of side chains to a polymer's backbone chain. It occurs by the replacement of a substituent on a monomer subunit by another covalently-bonded chain of that polymer; or, in the case of a graft copolymer, by a chain of another type. Branched polymers have more compact and symmetrical molecular conformations, and exhibit intra-heterogeneous dynamical behavior with respect to the unbranched polymers. In crosslinking rubber by vulcanization, short sulfur branches link polyisoprene chains into a multiple-branched thermosetting elastomer. Rubber can also be so completely vulcanized that it becomes a rigid solid, so hard it can be used as the bit in a smoking pipe. Polycarbonate chains can be crosslinked to form the hardest, most impact-resistant thermosetting plastic, used in safety glasses.

Hydrophobic collapse is a proposed process for the production of the 3-D conformation adopted by polypeptides and other molecules in polar solvents. The theory states that the nascent polypeptide forms initial secondary structure creating localized regions of predominantly hydrophobic residues. The polypeptide interacts with water, thus placing thermodynamic pressures on these regions which then aggregate or "collapse" into a tertiary conformation with a hydrophobic core. Incidentally, polar residues interact favourably with water, thus the solvent-facing surface of the peptide is usually composed of predominantly hydrophilic regions.
In IUPAC nomenclature of chemistry, a pendant group or side group is a group of atoms attached to a backbone chain of a long molecule, usually a polymer. Pendant groups are different from pendant chains, as they are neither oligomeric nor polymeric.

In biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, which are naturally encoded in the genome of organisms for the assembly of proteins. However, over 140 non-proteinogenic amino acids occur naturally in proteins and thousands more may occur in nature or be synthesized in the laboratory. Chemically synthesized amino acids can be called unnatural amino acids. Unnatural amino acids can be synthetically prepared from their native analogs via modifications such as amine alkylation, side chain substitution, structural bond extension cyclization, and isosteric replacements within the amino acid backbone. Many non-proteinogenic amino acids are important:













