| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
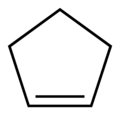
| Preferred IUPAC name Cyclopentene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.030 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 68.11 g/mol | ||
| Density | 0.771 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −135 °C (−211 °F; 138 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 44 to 46 °C (111 to 115 °F; 317 to 319 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −29 °C (−20 °F; 244 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds | Cyclopentadiene Cyclobutene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Cyclopentene is a chemical compound with the formula (CH2)3(CH)2. It is a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. It has few applications, and thus is mainly used as a minor component of gasoline, present in concentrations of less than 1%. [1] [2] It is one of the principal cycloalkenes.