| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methylpentane [1] | |||
| Other names Isohexane [2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 1730735 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.204 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | 2-methylpentane | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1208 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H14 | |||
| Molar mass | 86.178 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 653 mg mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | −160 to −146 °C; −256 to −231 °F; 113 to 127 K | ||
| Boiling point | 60 to 62 °C; 140 to 143 °F; 333 to 335 K | ||
| log P | 3.608 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 46.7 kPa (at 37.7 °C) | ||
Henry's law constant (kH) | 5.7 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| −75.26·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD) | 1.371 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) | 194.19 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 290.58 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −205.3 – −203.3 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    | |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H411 | |||
| P210, P261, P273, P301+P310, P331 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) | ||
| 306 °C (583 °F; 579 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–7% | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) | none [3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes | |||
Related compounds | 2-Ethyl-1-butanol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
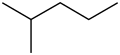
2-Methylpentane, trivially known as isohexane, is a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C6H14. It is a structural isomer of hexane composed of a methyl group bonded to the second carbon atom in a pentane chain.
As of early 1990s, it was present in American [4] and European [5] gasoline in small amounts, and by 2011 its share in US gas varied between 2 and 8%. [6] Using a quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) prediction model, 2-Methylpentane has a research octane number (RON) of 75, motor octane number (MON) of 77, and cetane number (CN) of 29. [7]