| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Ethynylbenzene | |
| Other names Phenylacetylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.861 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6 | |
| Molar mass | 102.133 g/mol |
| Density | 0.93 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) |
| Boiling point | 142 to 144 °C (288 to 291 °F; 415 to 417 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 28.7 (DMSO), [1] 23.2 (aq, extrapolated) [2] |
| −72.01·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
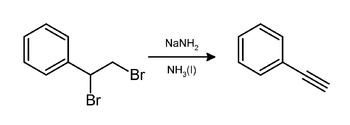
Phenylacetylene is an alkyne hydrocarbon containing a phenyl group. It exists as a colorless, viscous liquid. In research, it is sometimes used as an analog for acetylene; being a liquid, it is easier to handle than acetylene gas.