
Styrene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. Its structure consists of a vinyl group as substituent on benzene. Styrene is a colorless, oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations have a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene and several copolymers, and is typically made from benzene for this purpose. Approximately 25 million tonnes of styrene were produced in 2010, increasing to around 35 million tonnes by 2018.

Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone.

1,3-Butadiene is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene.

In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry.
In organic chemistry, arynes and benzynes are a class of highly reactive chemical species derived from an aromatic ring by removal of two substituents. Arynes are examples of didehydroarenes, although 1,3- and 1,4-didehydroarenes are also known. Arynes are examples of alkynes under high strain.
In organic chemistry, hydrocyanation is a process for conversion of alkenes to nitriles. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide and requires a catalyst. This conversion is conducted on an industrial scale for the production of precursors to nylon.

Chloroprene (IUPAC name 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH2=CCl−CH=CH2. Chloroprene is a colorless volatile liquid, almost exclusively used as a monomer for the production of the polymer polychloroprene, better known as neoprene, a type of synthetic rubber.
In polymer chemistry, a structural unit is a building block of a polymer chain. It is the result of a monomer which has been polymerized into a long chain.

Vinylacetylene is the organic compound with the formula C4H4. The colourless gas was once used in the polymer industry. It is composed of both alkyne and alkene groups and is the simplest enyne.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

1,4-Dihydropyridine (DHP) is an organic compound with the formula CH2(CH=CH)2NH. The parent compound is uncommon, but derivatives of 1,4-dihydropyridine are important commercially and biologically. The pervasive cofactors NADH and NADPH are derivatives of 1,4-dihydropyridine. 1,4-Dihydropyridine-based drugs are L-type calcium channel blockers, used in the treatment of hypertension. 1,2-Dihydropyridines are also known.
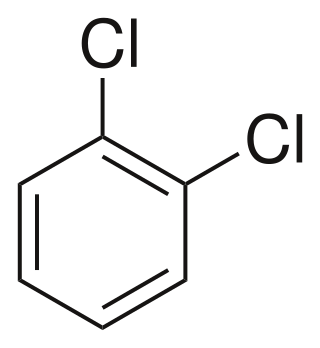
1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an aryl chloride and isomer of dichlorobenzene with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.

A dithiane is a heterocyclic compound composed of a cyclohexane core structure wherein two methylene bridges are replaced by sulfur. The three isomeric parent heterocycles are 1,2-dithiane, 1,3-dithiane and 1,4-dithiane. They are all colorless solids.

In organic chemistry, a xylylene (sometimes quinone-dimethide) is any of the constitutional isomers having the formula C6H4(CH2)2. These compounds are related to the corresponding quinones and quinone methides by replacement of the oxygen atoms by CH2 groups. ortho- and para-xylylene are best known, although neither is stable in solid or liquid form. The meta form is a diradical. Certain substituted derivatives of xylylenes are however highly stable, such as tetracyanoquinodimethane and the xylylene dichlorides.
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particular value in the petrochemical industry to manufacture p-xylene, styrene, and other aromatic compounds. Motivation for using transalkylation reactions is based on a difference in production and demand for benzene, toluene, and xylenes. Transalkylation can convert toluene, which is overproduced, into benzene and xylene, which are under-produced. Zeolites are often used as catalysts in transalkylation reactions.

Diethylbenzene (DEB) refers to any of three isomers with the formula C6H4(C2H5)2. Each consists of a benzene ring and two ethyl substituents. The meta and para have the greater commercial significance. All are colorless liquids.

The C4-benzenes are a class of organic aromatic compounds which contain a benzene ring and four other carbon atoms. There are three tetramethylbenzenes, six dimethylethylbenzenes, three diethylbenzenes, three isopropylmethylbenzenes, three n-propylmethylbenzenes and four butylbenzenes. The saturated compounds have formula C10H14 and molecular weight 134.22 g/mol. C4-benzenes are found in petroleum. Petrol (gasoline) can contain 5-8% C4-benzenes.
The diisopropylbenzenes(DIPB) are organic compounds with the formula C6H4(CH(CH3)2)2. Three isomers exist: 1,2- 1,3-, and 1,4-diisopropylbenzene. All are colorless liquids, immiscible in water, with similar boiling points. They are classified are aromatic hydrocarbons bearing a pair of isopropyl (CH(CH3)2) substituents. DIPB has been referred to as "a common diluent" alongside hexane.
The chemical compound xylylene dichloride (C6H4(CH2Cl)2) is a white to light yellow sandlike solid. This compound can be classified as a benzyl halide. Xylylene dichloride is used as a vulcanizing agent to harden rubbers. It catalyzes the crosslinking of phenolic resins.















