
Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

The Chaetothyriales are an order of ascomycetous fungi in the class Eurotiomycetes and within the subclass Chaetothyriomycetidae. The order was circumscribed in 1987 by mycologist Margaret Elizabeth Barr-Bigelow.
Ramularia menthicola is a species of fungus in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. It is a plant pathogen that infects mint. It was formally described as a new species by the Italian mycologist Pier Andrea Saccardo in 1886. In his 1998 monograph on phytopathogenic Hyphomycetes, Uwe Braun suggests that Ramularia menthae should be considered a synonym to Ramularia lamii, but the name remains in use in the scientific literature, and is accepted as a valid species by Index Fungorum.

The Pleosporales is the largest order in the fungal class Dothideomycetes. By a 2008 estimate, it contained 23 families, 332 genera and more than 4700 species. The majority of species are saprobes on decaying plant material in fresh water, marine, or terrestrial environments, but several species are also associated with living plants as parasites, epiphytes or endophytes. The best studied species cause plant diseases on important agricultural crops e.g. Cochliobolus heterostrophus, causing southern corn leaf blight on maize, Phaeosphaeria nodorum causing glume blotch on wheat and Leptosphaeria maculans causing a stem canker on cabbage crops (Brassica). Some species of Pleosporales occur on animal dung, and a small number occur as lichens and rock-inhabiting fungi.
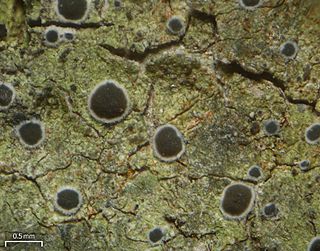
The Pilocarpaceae are a family of crustose lichens in the order Lecanorales. The species of this family have a cosmopolitan distribution and have been found in a variety of climatic regions. Pilocarpaceae was circumscribed by Alexander Zahlbruckner in Adolf Engler's influential 1905 work Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien.
Moniliella is a genus of fungi in the subdivision Ustilaginomycotina. It is in the monotypic family MoniliellaceaeQ.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & Boekhout, which is in the monotypic order MoniliellalesQ.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & Boekhout which is in the monotypic class MoniliellomycetesQ.M. Wang, F.Y. Bai & Boekhout.
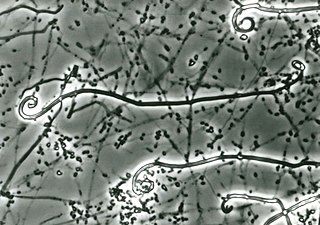
Uncinocarpus is a genus of fungi within the Onygenaceae family. The name is derived from the Latin word uncinus, meaning "hook" and the Greek word karpos (καρπός), meaning "fruit". It was distinguished from the genus Gymnoascus based on keratinolytic capacity, ascospore morphology and the development of hooked, occasionally spiraling appendages. Alternatively, Uncinocarpus species may possess helically coiled or smooth, wavy appendages, or lack appendages altogether, an example of such species being U. orissi.
Gabarnaudia is a genus of anamorphic fungi that was placed in the family Ceratocystidaceae, until phylogenetic analysis by Hausner and Reid (2004) and De Beer et al. (2013a) showed that Gabarnaudia fimicolaG. betae and G. humicola clustered within genus Sphaeronaemella.

Cordana is an ascomycete fungus genus. In 2020, it was placed within the monotypic family of Cordanaceae, and within the order Coniochaetales.

Taeniolella is a genus of asexual fungi hyphomycetes in the family Mytilinidiaceae. Some of the species are lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling), others are saprophytic, while others are endophytic. The genus was circumscribed in 1958 by Canadian mycologist Stanley John Hughes, with Taeniolella exilis as the type species. Major revisions of the lichenicolous species in the genus were published in 2016 and 2018.

Engyodontium is a genus of fungi belonging to the group Hyphomycetes and contains about 6 species. This fungus was formerly included in Beauveria, but is now recognized as a distinct genus.

Exophiala phaeomuriformis is thermophilic fungus belonging to the genus Exophiala and the family Herpotrichiellaceae. it is a member of the group of fungi known as black yeasts, and is typically found in hot and humid locations, such as saunas, bathrooms, and dishwashers. This species can cause skin infections and is typically classified as a Biosafety Risk Group 2 agent.
Cladophialophora arxii is a black yeast shaped dematiaceous fungus that is able to cause serious phaeohyphomycotic infections. C. arxii was first discovered in 1995 in Germany from a 22-year-old female patient suffering multiple granulomatous tracheal tumours. It is a clinical strain that is typically found in humans and is also capable of acting as an opportunistic fungus of other vertebrates Human cases caused by C. arxii have been reported from all parts of the world such as Germany and Australia.
Knufia is a genus of fungi in the family Trichomeriaceae.
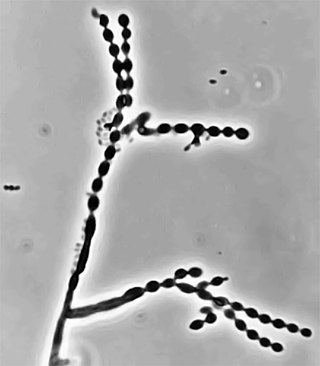
Cladophialophora is a genus of fungi in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It has 35 species. The genus contains black yeast-like fungi, some of which are species of important medical significance. Cladophialophora bantiana causes the rare brain disease cerebral phaeohyphomycosis. Cladophialophora carrionii is a common cause of chromoblastomycosis in semi-arid climates. Some of the species are endophytes–associating with plants. For example, Cladophialophora yegresii is a cactus endophyte, which is sometimes introduced into humans via cactus spines.

Rhinocladiella is a genus of fungi in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It has 17 species. The genus was circumscribed by Swedish botanist John Axel Nannfeldt in 1934 with R. atrovirens as the type species.
Dactylaria is a genus of fungi belonging to an unknown family. According to Wijayawardene et al. 2020; the genus was placed in order Helotiales genera incertae sedis.
Monodictys is a genus of fungi of uncertain familial and ordinal placement in the class Ascomycetes. The genus was circumscribed by Welsh-born Canadian mycologist Stanley Hughes in 1956. He assigned Monodictys putredinis as the type species.
Leptodontidium trabinellum is a species of fungus in the family Leptodontidiaceae.
Quadracaea is a fungal genus in the division Ascomycota. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the division is unknown, and it has not yet been placed with certainty into any class, order, or family. The genus contains three species of hyphomycetes. Quadracea is characterised by its distinctive spore-producing structures and the unique appearance and morphology of its spores.










