Related Research Articles
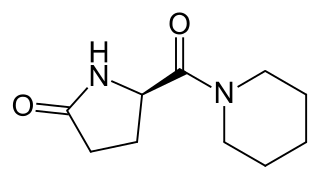
Fasoracetam is an experimental drug of the racetam group which was never marketed. It is a putative nootropic that failed to show sufficient efficacy in clinical trials for vascular dementia. The drug was also subsequently repurposed for treatment of a variety of other conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but effectiveness for ADHD was disappointing and development of fasoracetam for most other conditions has been discontinued as well. In any case, it remains under development for treatment of DiGeorge syndrome.

Lubazodone is an experimental antidepressant which was under development by Yamanouchi for the treatment for major depressive disorder in the late 1990s and early 2000s but was never marketed. It acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist, and hence has the profile of a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). The drug has good selectivity against a range of other monoamine receptors, with its next highest affinities being for the α1-adrenergic receptor and the 5-HT2C receptor. Lubazodone is structurally related to trazodone and nefazodone, but is a stronger serotonin reuptake inhibitor and weaker as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist in comparison to them and is more balanced in its actions as a SARI. It reached phase II clinical trials for depression, but development was discontinued in 2001 reportedly due to the "erosion of the SSRITooltip selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor market in the United States".

Amitifadine is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) or so-called triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI) which is or was being developed by Euthymics Bioscience. It was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder, but in May 2013, it was reported that the drug failed to show superior efficacy to placebo in a phase IIb/IIIa clinical trial. it was suggested that this may have been due to the drug being underdosed. In September 2017, development of amitifadine for the treatment of major depressive disorder was finally officially discontinued. As of September 2017, it is still listed as being under development for the treatment of alcoholism and smoking withdrawal.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is an atypical antipsychotic medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.

Rapastinel is a novel antidepressant that was under development by Allergan as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression. It is a centrally active, intravenously administered amidated tetrapeptide that acts as a novel and selective modulator of the NMDA receptor. The drug is a rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant as well as robust cognitive enhancer by virtue of its ability to enhance NMDA receptor-mediated signal transduction and synaptic plasticity.
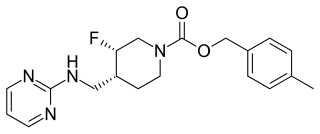
Rislenemdaz is an orally active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.
TGBA01AD (also known as FKB01MD) is a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptor agonist, and 5-HT2 receptor antagonist which is under development by Fabre-Kramer for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It has been in phase II clinical trials since 2009, and as of January 2016, remains in this phase of development.

Toludesvenlafaxine, also formerly known as ansofaxine and sold under the brand name Ruoxinlin, is an antidepressant which is approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder in China. It is also under development for use in other countries like the United States. It is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) and was developed by Luye Pharma Group.

Zelquistinel is an orally active small-molecule NMDA receptor modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by Gate Neurosciences, and previously by Allergan.
Deudextromethorphan/quinidine is a combination of deudextromethorphan and quinidine (Q) which is under development by Avanir Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of a variety of neurological and psychiatric indications. The pharmacological profile of d-DXM/Q is similar to that of dextromethorphan/quinidine (DXM/Q). DXM and d-DXM act as σ1 receptor agonists, NMDA receptor antagonists, and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, among other actions, while quinidine is an antiarrhythmic agent acting as a CYP2D6 inhibitor. Quinidine inhibits the metabolism of DXM and d-DXM into dextrorphan (DXO), which has a different pharmacological profile from DXM. Deuteration of DXM hinders its metabolism by CYP2D6 into DXO, thereby allowing for lower doses of quinidine in the combination. This in turn allows for lower potential for drug interactions and cardiac adverse effects caused by quinidine. As of September 2020, d-DXM/Q is in phase 3 clinical trials for agitation, phase 2/3 trials for schizophrenia, and phase 2 trials for brain injuries, impulse control disorders, major depressive disorder, and neurodegenerative disorders.
SYT-510 is an endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor, or "selective endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor" ("SERI"), which is under development for the treatment of anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and traumatic stress disorders. It is said to mildly and selectively increase levels of endocannabinoids like anandamide via inhibition of a newly identified biological target. As of January 2024, the drug is in the preclinical stage of development or is entering phase 1 clinical trials for the preceding indications. It is under development by a pharmaceutical company called Synendos Therapeutics.

Traneurocin, also known as cycloprolylglycine (CPG), is a racetam-like drug which is under development for the treatment of COVID-19, Alzheimer's disease, fragile X syndrome, Rett syndrome, major depressive disorder, and other neurological disorders. In the case of COVID-19, it is specifically being developed for treatment of COVID-19-induced neuropathy.
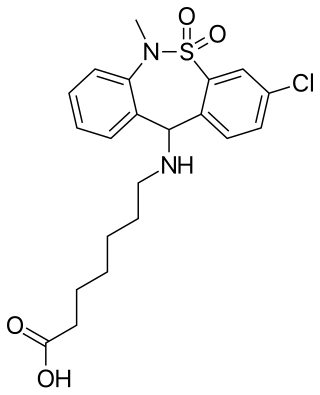
Tianeptine/naloxone, or naloxone/tianeptine, is an extended-release combination of tianeptine, an atypical μ-opioid receptor agonist, and naloxone, an orally inactive μ-opioid receptor antagonist, which was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and neurocognitive dysfunction associated with corticosteroid use but was never marketed.
PRAX-114 is a neurosteroid and GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder, essential tremor, depressive disorders, and epilepsy. It was also under development for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but development for this indication was discontinued. The drug is taken by mouth.
Pegipanermin is a tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) inhibitor which is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment, major depressive disorder, and other indications. It is described as having potential anti-inflammatory effects. It is administered by subcutaneous injection.
ML-007 is a selective muscarinic acetylcholine M1 and M4 receptor agonist which is under development for the treatment of schizophrenia, psychotic disorders, and dyskinesias. It is being developed in combination with a peripherally selective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. The drug is taken by mouth.

AZD-2327 is a δ-opioid receptor agonist which was under development for the treatment of depressive disorders and anxiety disorders but was never marketed. It is taken by mouth.

AZD-7268 is a δ-opioid receptor agonist which was under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder but was never marketed. It is taken by mouth.
OPC-64005 is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), or "triple reuptake inhibitor" (TRI), which is under development for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It was also under development for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but development for this indication was discontinued. It is taken by mouth.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "SNG 12". AdisInsight. 23 September 2022. Retrieved 21 October 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 "Delving into the Latest Updates on Synapsinae with Synapse". Synapse. 28 September 2024. Retrieved 21 October 2024.
- 1 2 "A phase III study for SNG-12 in depression and Suicidal ideation". AdisInsight. 16 March 2021. Retrieved 21 October 2024.
- ↑ "Synapsinae Drug Profile". Ozmosi. 7 May 2024. Retrieved 21 October 2024.