
Hydrangea, commonly named the hortensia, is a genus of more than 75 species of flowering plants native to Asia and the Americas. By far the greatest species diversity is in eastern Asia, notably China, Korea, and Japan. Most are shrubs 1–3 m tall, but some are small trees, and others lianas reaching up to 30 m (100 ft) by climbing up trees. They can be either deciduous or evergreen, though the widely cultivated temperate species are all deciduous.

Dianthus caryophyllus, commonly known as the carnation or clove pink, is a species of Dianthus. It is likely native to the Mediterranean region but its exact range is unknown due to extensive cultivation for the last 2,000 years.
A pH indicator is a halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a solution so the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by changes in absorption and/or emission properties. Hence, a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. Normally, the indicator causes the color of the solution to change depending on the pH. Indicators can also show change in other physical properties; for example, olfactory indicators show change in their odor. The pH value of a neutral solution is 7.0 at 25°C (standard laboratory conditions). Solutions with a pH value below 7.0 are considered acidic and solutions with pH value above 7.0 are basic. Since most naturally occurring organic compounds are weak electrolytes, such as carboxylic acids and amines, pH indicators find many applications in biology and analytical chemistry. Moreover, pH indicators form one of the three main types of indicator compounds used in chemical analysis. For the quantitative analysis of metal cations, the use of complexometric indicators is preferred, whereas the third compound class, the redox indicators, are used in redox titrations (titrations involving one or more redox reactions as the basis of chemical analysis).
Benedict's reagent is a chemical reagent and complex mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. It is often used in place of Fehling's solution to detect the presence of reducing sugars. The presence of other reducing substances also gives a positive result. Such tests that use this reagent are called the Benedict's tests. A positive test with Benedict's reagent is shown by a color change from clear blue to brick-red with a precipitate.
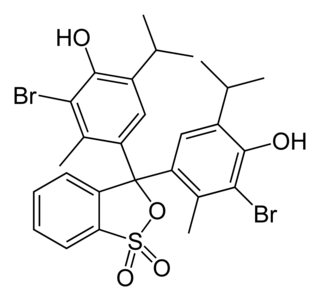
Bromothymol blue is a pH indicator. It is mostly used in applications that require measuring substances that would have a relatively neutral pH. A common use is for measuring the presence of carbonic acid in a liquid. It is typically sold in solid form as the sodium salt of the acid indicator.

The enzyme alkaline phosphatase has the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of E. coli bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia.

Strongylodon macrobotrys, commonly known as jade vine, emerald vine or turquoise jade vine, is a species of leguminous perennial liana endemic to the tropical forests of the Philippines. Its local name is tayabak. A member of the Fabaceae, it is closely related to beans such as kidney bean and runner bean. Strongylodon macrobotrys is pollinated by bats.

The Wahiawa Botanical Garden, 27 acres (11 ha) is a botanical garden on a high plateau in central Oʻahu, Hawaiʻi, United States, located between the Wai'anae and Ko'olau mountain ranges. It is one of the Honolulu Botanical Gardens, and home to a collection of tropical flora requiring a relatively cool environment, with emphasis on native Hawaiian plants. It is nicknamed the "tropical jewel" of the Botanical Gardens. The Garden's site began in the 1920s, when the Hawaiian Sugar Planters' Association leased land from the State of Hawaiʻi for experimental tree planting. Most of the Garden's large trees date from that era. The property was transferred to Honolulu in 1950, and opened as a botanical garden in 1957. It is open seven days a week, from 9am to 4 pm.

Hydrangea macrophylla is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, native to Japan. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall by 2.5 m (8 ft) broad with large heads of pink or blue flowers in summer and autumn. Common names include bigleaf hydrangea, French hydrangea, lacecap hydrangea, mophead hydrangea, penny mac and hortensia. It is widely cultivated in many parts of the world in many climates. It is not to be confused with H. aspera 'Macrophylla'.

Wisteria floribunda, common name Japanese wisteria, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to Japan. Growing to 9 m (30 ft), Wisteria floribunda is a woody, deciduous twining climber. It was first brought from Japan to the United States in the 1830s. Since then, it has become one of the most highly romanticized flowering garden plants. It is also a common subject for bonsai, along with Wisteria sinensis.

Ziziphus mauritiana, also known as Indian jujube, Indian plum, Chinese date, Chinee apple, ber,beri and dunks is a tropical fruit tree species belonging to the family Rhamnaceae. It is often confused with the closely related Chinese jujube, but whereas Z. jujuba prefers temperate climates, Z. mauritiana is tropical to subtropical.

The red cabbage is a kind of cabbage, also known as Blaukraut after preparation. Its leaves are colored dark red/purple. However, the plant changes its color according to the pH value of the soil due to a pigment belonging to anthocyanins. In acidic soils, the leaves grow more reddish; in neutral soils, they will grow more purple, while an alkaline soil will produce rather greenish-yellow colored cabbages. This explains the fact that the same plant is known by different colors in various regions. It can be found in all of Europe, throughout the Americas, in China, and especially in Africa.

Litmus is a water-soluble mixture of different dyes extracted from lichens. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator, used to test materials for acidity. In an acidic medium, blue litmus paper turns red, while in a basic or alkaline medium, red litmus paper turns blue.

Alkaline diet describes a group of loosely related diets based on the misconception that different types of food can have an effect on the pH balance of the body. It originated from the acid ash hypothesis, which primarily related to osteoporosis research. Proponents of the diet believe that certain foods can affect the acidity (pH) of the body and that the change in pH can therefore be used to treat or prevent disease. However, their claims are false, and there is no evidence supporting the claimed mechanisms of this diet, which is not recommended by dietitians or other health professionals.

Malvin is a naturally occurring chemical of the anthocyanin family.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

Isosaccharinic acid (ISA) is a six-carbon sugar acid which is formed by the action of calcium hydroxide on lactose and other carbohydrates. It is of interest because it may form in intermediate-level nuclear waste stores when cellulose is degraded by the calcium hydroxide in cements such as Portland cement. The calcium salt of the alpha form of ISA is very crystalline and quite insoluble in cold water, but in hot water it is soluble.
Copigmentation is a phenomenon where pigmentation due to anthocyanidins is reinforced by the presence of other colorless flavonoids known as cofactors or “copigments”. This occurs by the formation of a non-covalently-linked complex.

Ipomoea arborescens, the tree morning glory, is a rapidly-growing, semi-succulent flowering tree in the family Convolvulaceae. This tropical plant is mostly found in Mexico, and flowers in late autumn and winter. Its common name in Nahuatl is Cazahuatl or Cazahuate.

Strongylodon juangonzalezii, commonly called JC's vine or purple jade vine, is a species of leguminous perennial liana endemic to the tropical forests of the Philippines. It bears a cluster of large flowers that are initially lilac to purple in color, but become a striking blue as they mature.

















