
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.

Polyphenols are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments.

Punicalagin is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found in forms alpha and beta in pomegranates, in Terminalia catappa and Terminalia myriocarpa, and in Combretum molle, the velvet bushwillow, a plant species found in South Africa. These three genera are all Myrtales and the last two are both Combretaceae.

Hymenaea L. is a genus in the flowering plant family Fabaceae. Of fourteen living species in the genus, all but one are native to the tropics of the Americas, with one additional species on the east coast of Africa. Some authors place the African species in a separate monotypic genus, Trachylobium. In the Neotropics, Hymenaea is distributed through the Caribbean islands, and from southern Mexico to Brazil. Linnaeus named the genus in 1753 in Species Plantarum for Hymenaios, the Greek god of marriage ceremonies. The name is a reference to the paired leaflets.

Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Ethyl gallate is a food additive with E number E313. It is the ethyl ester of gallic acid. Ethyl gallate is added to food as an antioxidant.

The flavanonols are a class of flavonoids that use the 3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone.

Astilbin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. Astilbin is the (2R-trans)-isomer; neoisoastilbin is the (2S-cis)-isomer and isoastilbin is the (2R-cis)-isomer.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.
Hymenaea martiana is a tree species in the genus Hymenaea found in Brazil and Paraguay.

Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compound and dimethoxybenzene that is commonly found as a plant metabolite.

Acutissimin A is a flavono-ellagitannin, a type of tannin formed from the linking of a flavonoid with an ellagitannin.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols refers to phenol functional group that is found in natural products. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

The grape reaction product is a phenolic compound explaining the disappearance of caftaric acid from grape must during processing. It is also found in aged red wines. Its enzymatic production by polyphenol oxidase is important in limiting the browning of musts, especially in white wine production. The product can be recreated in model solutions.

Astringin is a stilbenoid, the 3-β-D-glucoside of piceatannol. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis or Picea abies.

Wine is a complex mixture of chemical compounds in a hydro-alcoholic solution with a pH around 4.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the sarcotestas, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of pomegranates.
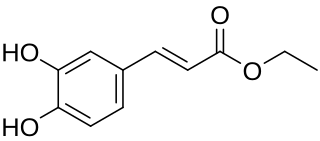
Ethyl caffeate is an ester of a hydroxycinnamic acid, a naturally occurring organic compound.
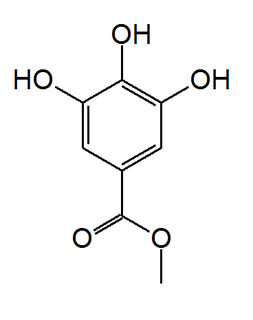
Methyl gallate is a phenolic compound. It is the methyl ester of gallic acid.


















