
Betula pendula, commonly known as silver birch, warty birch, European white birch, or East Asian white birch, is a species of tree in the family Betulaceae, native to Europe and parts of Asia, though in southern Europe, it is only found at higher altitudes. Its range extends into Siberia, China, and southwest Asia in the mountains of northern Turkey, the Caucasus, and northern Iran. It has been introduced into North America, where it is known as the European white birch, and is considered invasive in some states in the United States and parts of Canada. The tree can also be found in more temperate regions of Australia.

Strychnos is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae. The genus includes about 100 accepted species of trees and lianas, and more than 200 that are as yet unresolved. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare.

Betula papyrifera is a short-lived species of birch native to northern North America. Paper birch is named for the tree's thin white bark, which often peels in paper like layers from the trunk. Paper birch is often one of the first species to colonize a burned area within the northern latitudes, and is an important species for moose browsing. The wood is often used for pulpwood and firewood.

Diospyros melanoxylon, the Coromandel ebony or East Indian ebony, is a species of flowering tree in the family Ebenaceae native to India and Sri Lanka; it has a hard, dry bark. Its common name derives from Coromandel, the coast of southeastern India. Locally it is known as temburini or by its Hindi name tendu. In Odisha, Jharkhand, and Assam, it is known as kendu. The leaves can be wrapped around tobacco to create the Indian beedi, which has outsold conventional cigarettes in India. The olive-green fruit of the tree is edible
Hymenaea protera is an extinct prehistoric leguminous tree, the probable ancestor of present-day Hymenaea species. Most neotropical ambers come from its fossilized resin, including the famous Dominican amber.

Hymenaea L. is a genus in the flowering plant family Fabaceae. Of fourteen living species in the genus, all but one are native to the tropics of the Americas, with one additional species on the east coast of Africa. Some authors place the African species in a separate monotypic genus, Trachylobium. In the Neotropics, Hymenaea is distributed through the Caribbean islands, and from southern Mexico to Brazil. Linnaeus named the genus in 1753 in Species Plantarum for Hymenaios, the Greek god of marriage ceremonies. The name is a reference to the paired leaflets.
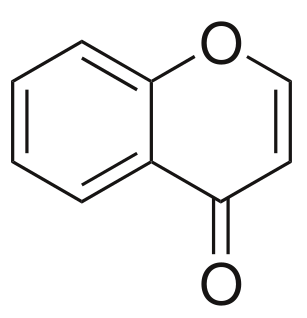
Chromone is a derivative of benzopyran with a substituted keto group on the pyran ring. It is an isomer of coumarin.

Hymenaea courbaril, the courbaril or West Indian locust, is a tree common in the Caribbean, Central America, and South America. It is a hardwood that is used for furniture, flooring, and decoration. Its hard fruit pods have edible dry pulp surrounding the seeds. Its sap, called animé, is used for incense, perfume, and varnish.

Vachellia nilotica is a flowering plant tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Africa, the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent. It is also a Weed of National Significance in Australia as well as a Federal Noxious Weed in the United States.

Eucryphia cordifolia, the ulmo, is a species of tree in the family Cunoniaceae. It is found in Chile and Argentina. It is threatened by logging and habitat loss. The natural habitat is along the Andes Range from 38 to 43°S, and up to 700 meters (2300 ft) above sea level. It is a very elegant tree with a thick trunk and wide crown and can become over 12 m (40 ft) high. It blooms in February and March, depending on latitude and altitude. The fruit is a capsule about 1.5 cm (0.6 in) length.

Mangifera indica, commonly known as mango, is a species of flowering plant in the sumac and poison ivy family Anacardiaceae. It is native to the Indian subcontinent where it is indigenous. Hundreds of cultivated varieties have been introduced to other warm regions of the world. It is a large fruit-tree, capable of growing to a height and crown width of about 30 metres (100 ft) and trunk circumference of more than 3.7 metres (12 ft).

Hymenaea verrucosa is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the paraphyletic subfamily Caesalpinioideae. It is a large tree native to the tropical regions of East Africa and is cultivated in many tropical parts of the world. The species is currently treated as a species of Hymenaea, though a few authors isolate it into a separate monospecific genus Trachylobium as Trachylobium verrucosum.

Astilbin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. Astilbin is the (2R-trans)-isomer; neoisoastilbin is the (2S-cis)-isomer and isoastilbin is the (2R-cis)-isomer.
Martiana clausa is a species of crab in the family Pseudothelphusidae, the only species in the genus Martiana.
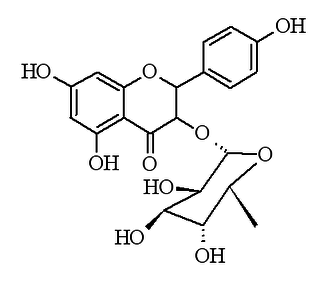
Engeletin is a flavanonol glucoside, a phenolic compound found in wine and isolated from the bark of Hymenaea martiana.

Persoonia oxycoccoides is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to New South Wales. It is a spreading to prostrate shrub with smooth bark, hairy young branchlets, elliptic to egg-shaped leaves and yellow flowers arranged in groups of up to thirteen along a rachis that continues to grow after flowering.

Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section Populus, of the Populus genus.

Ceriops tagal, commonly known as spurred mangrove or Indian mangrove, is a mangrove tree species in the family Rhizophoraceae. It is a protected tree in South Africa. The specific epithet tagal is a plant name from the Tagalog language.

Persoonia amaliae is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a shrub or small tree with hairy young branches, spatula-shaped to lance-shaped leaves and yellow flowers in groups of up to eleven.

Hymenaea stiginocarpa is an irregularly shaped, mostly 6–9 m (20–30 ft) high tree that has been assigned to the pea family. It has a twisted spindle-shaped trunk, a very rough grey bark, and reddish-brown twigs. The deciduous leaves consist of two large asymmetrical leaflets with an entire margin. The flowers occur in clusters of up to thirty at the end of the branches. It produces edible, highly appreciated fruits, which are often collected from the wild and used by local people. The vernacular name of this species in Brazil is jatobá do cerrado.

















