
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Harmala alkaloids are several alkaloids that act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These alkaloids are found in the seeds of Peganum harmala, as well as Banisteriopsis caapi (ayahuasca), leaves of tobacco and coffee beans. The alkaloids include harmine, harmaline, harmalol, and their derivatives, which have similar chemical structures, hence the name "harmala alkaloids". These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. Harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring beta-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine Banisteriopsis caapi. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in B. caapi and P. harmala. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs). They can stimulate the central nervous system by inhibiting the metabolism of monoamine compounds such as serotonin and norepinephrine.

Tetrahydroharmine (THH) is a fluorescent indole alkaloid that occurs in the tropical liana species Banisteriopsis caapi.

Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in the United States, but is approved in other Western countries such as Canada, the UK and Australia. It is produced by affiliates of the Hoffmann–La Roche pharmaceutical company. Initially, Aurorix was also marketed by Roche in South Africa, but was withdrawn after its patent rights expired and Cipla Medpro's Depnil and Pharma Dynamic's Clorix became available at half the cost.

Brofaromine is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) discovered by Ciba-Geigy. The compound was primarily researched in the treatment of depression and anxiety but its development was dropped before it was brought to market.
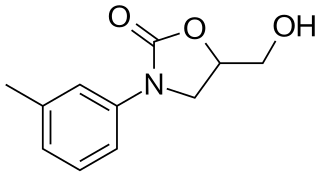
Toloxatone (Humoryl) is an antidepressant launched in 1984 in France by Sanofi Aventis for the treatment of depression. It was discontinued in 2002. It acts as a selective reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA).

Pargyline, sold under the brand name Eutonyl among others, is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medication which has been used to treat hypertension but is no longer marketed. It has also been studied as an antidepressant, but was never licensed for use in the treatment of depression. The drug is taken by mouth.

Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAO-B, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.
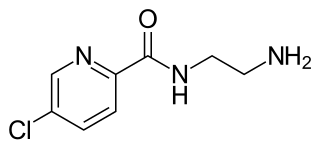
Lazabemide is a reversible and selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) that was under development as an antiparkinsonian agent but was never marketed.

Cimoxatone is a reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA). It has a significant food interaction–related adverse effect in combination with tyramine. It was never marketed.

Bifemelane (INN) (Alnert, Celeport), or bifemelane hydrochloride (JAN), also known as 4-(O-benzylphenoxy)-N-methylbutylamine, is an antidepressant and cerebral activator that was widely used in the treatment of cerebral infarction patients with depressive symptoms in Japan, and in the treatment of senile dementia as well. It also appears to be useful in the treatment of glaucoma. It has been discontinued in Japan since 1998, when it was removed from the market reportedly for lack of effectiveness.

Mebanazine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was previously used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.

Ladostigil is a novel neuroprotective agent being investigated for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body disease, and Parkinson's disease. It was developed from structural modification of rasagiline.
Metralindole (Inkazan) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) which was investigated in Russia as a potential antidepressant. It is structurally and pharmacologically related to pirlindole.

Amiflamine (FLA-336) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), thereby being a RIMA, and, to a lesser extent, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO), as well as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA). It is a derivative of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. The (+)-enantiomer is the active stereoisomer.
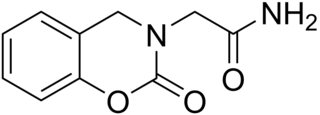
Caroxazone is an antidepressant which was formerly used for the treatment of depression but is now no longer marketed. It acts as a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (RIMA) of both MAO-A and MAO-B subtypes, with five-fold preference for the latter.

Almoxatone (MD-780,236) is a selective and reversible inhibitor of MAO-B. It was patented as an antidepressant and antiparkinsonian agent but was never marketed.
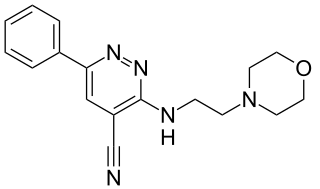
Bazinaprine (SR-95,191) is an experimental drug candidate. It is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) which is believed to be useful for the treatment of depression. The drug strongly inhibits type A monoamine oxidase, but only weakly inhibits type B. The effects of the drug are reversible in vivo, but not in vitro. In studies, the chemical has been shown to not interact in vivo with other neurotransmitter or drug receptor sites.

Eprobemide (INN) is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an antidepressant in Russia. It is a non-competitive reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A that exhibits selective action on serotonin deamination. Eprobemide differs from moclobemide only in the linker that connects the morpholine fragment with the chlorobenzamide — moclobemide has two carbon atoms while eprobemide has three. Its registration was cancelled on December 30, 2003.

Desmethylselegiline (DMS), also known as norselegiline or as N-propargyl-L-amphetamine, is an active metabolite of selegiline, a medication used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and depression.



















