Related Research Articles

H2 antagonists, sometimes referred to as H2RAs and also called H2 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the histamine H2 receptors of the parietal cells in the stomach. This decreases the production of stomach acid. H2 antagonists can be used in the treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease. They have been surpassed by proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The PPI omeprazole was found to be more effective at both healing and alleviating symptoms of ulcers and reflux oesophagitis than the H2 blockers ranitidine and cimetidine.

Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discovered in 1910, it has been considered a local hormone (autocoid) because it lacks the classic endocrine glands to secrete it; however, in recent years, histamine has been recognized as a central neurotransmitter. Histamine is involved in the inflammatory response and has a central role as a mediator of itching. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by basophils and by mast cells found in nearby connective tissues. Histamine increases the permeability of the capillaries to white blood cells and some proteins, to allow them to engage pathogens in the infected tissues. It consists of an imidazole ring attached to an ethylamine chain; under physiological conditions, the amino group of the side-chain is protonated.
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines.

Itch is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itches leads to a scratch reflex.

Hydroxyzine, sold under the brand names Atarax and Vistaril among others, is an antihistamine medication. It is used in the treatment of itchiness, insomnia, anxiety, and nausea, including that due to motion sickness. It is used either by mouth or injection into a muscle.

Histamine H3 receptors are expressed in the central nervous system and to a lesser extent the peripheral nervous system, where they act as autoreceptors in presynaptic histaminergic neurons and control histamine turnover by feedback inhibition of histamine synthesis and release. The H3 receptor has also been shown to presynaptically inhibit the release of a number of other neurotransmitters (i.e. it acts as an inhibitory heteroreceptor) including, but probably not limited to dopamine, GABA, acetylcholine, noradrenaline, histamine and serotonin.

Betahistine, sold under the brand name Serc among others, is an anti-vertigo medication. It is commonly prescribed for balance disorders or to alleviate vertigo symptoms. It was first registered in Europe in 1970 for the treatment of Ménière's disease, but current evidence does not support its efficacy in treating it.
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonists, excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists, and excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors.

The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of rhodopsin-like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system. The H1 receptor is linked to an intracellular G-protein (Gq) that activates phospholipase C and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) signalling pathway. Antihistamines, which act on this receptor, are used as anti-allergy drugs. The crystal structure of the receptor has been determined (shown on the right/below) and used to discover new histamine H1 receptor ligands in structure-based virtual screening studies.
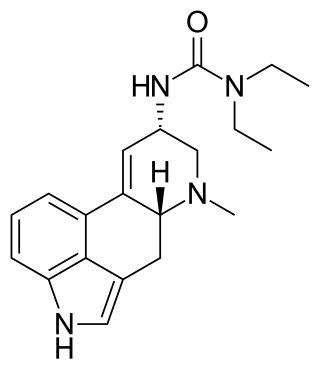
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

Thioperamide is a potent HRH4 antagonist and selective HRH3 antagonist capable of crossing the blood–brain barrier. It was used by Jean-Charles Schwartz in his early experiments regarding the H3 receptor. Thioperamide was found to be an antagonist of histamine autoreceptors, which negatively regulate the release of histamine. The drug enhances the activity of histaminergic neurons by blocking autoreceptors, leading to greater release of histamine.

Ciproxifan is an extremely potent histamine H3 inverse agonist/antagonist.

Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use.
A histamine agonist is a drug which causes increased activity at one or more of the four histamine receptor subtypes.
An H3 receptor antagonist is a type of antihistaminic drug used to block the action of histamine at H3 receptors.

Oxaprotiline, also known as hydroxymaprotiline, is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor belonging to the tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) family and is related to maprotiline. Though investigated as an antidepressant, it was never marketed.
Pitolisant, sold under the brand name Wakix among others, is a medication used for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness in adults with narcolepsy. It is a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/inverse agonist (an antihistamine drug specific to that kind of receptors). It represents the first commercially available medication in its class, so that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) declares it a first-in-class medication. Pitolisant enhances the activity of histaminergic neurons in the brain that function to improve a person's wakefulness.
Monoaminergic means "working on monoamine neurotransmitters", which include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and histamine.
Adenosinergic means "working on adenosine".
A glycinergic agent is a chemical which functions to directly modulate the glycine system in the body or brain. Examples include glycine receptor agonists, glycine receptor antagonists, and glycine reuptake inhibitors.
References
- ↑ "Histaminergic - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2023-11-04.
- ↑ "Histamine Agents | DrugBank Online". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 2023-11-04.