
Dienestrol, also known as dienoestrol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen medication of the stilbestrol group which is or was used to treat menopausal symptoms in the United States and Europe. It has been studied for use by rectal administration in the treatment of prostate cancer in men as well. The medication was introduced in the U.S. in 1947 by Schering as Synestrol and in France in 1948 as Cycladiene. Dienestrol is a close analogue of diethylstilbestrol. It has approximately 223% and 404% of the affinity of estradiol at the ERα and ERβ, respectively.

Chlorotrianisene (CTA), also known as tri-p-anisylchloroethylene (TACE) and sold under the brand name Tace among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen related to diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was previously used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency in women and prostate cancer in men, among other indications, but has since been discontinued and is now no longer available. It is taken by mouth.
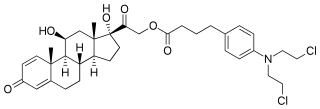
Prednimustine, sold under the brand names Mostarina and Sterecyst, is a medication which is used in chemotherapy in the treatment of leukemias and lymphomas. It is the ester formed from two other drugs, prednisolone and chlorambucil. Rarely, it has been associated with myoclonus.

Trioxifene, or as the salt trioxifene mesylate (USAN), is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with competitive binding activity against estradiol for the ERα and antagonistic activity against ERα-mediated gene expression, that was under preclinical and clinical development by Eli Lilly and Company for breast cancer and prostate cancer, but was abandoned. Its affinity for the rat estrogen receptor was reported to be 20% relative to estradiol.

Hexestrol, sold under the brand name Synestrol among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen which was previously used for estrogen replacement therapy and in the treatment of certain hormone-dependent cancers as well as gynecological disorders but is mostly no longer marketed. It has also been used in the form of esters such as hexestrol diacetate and hexestrol dipropionate. Hexestrol and its esters are taken by mouth, held under the tongue, or via injection into muscle.
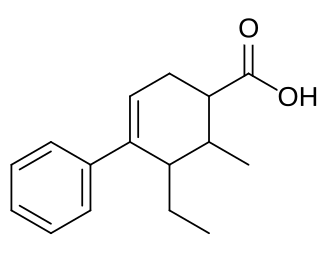
Fenestrel is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen that was developed as a postcoital contraceptive in the 1960s but was never marketed. Synthesized by Ortho Pharmaceutical in 1961 and studied extensively, it was coined the "morning-after-pill" or "postcoital antifertility agent". Fenestrel is a seco analogue of doisynolic acid, and a member of the cyclohexenecarboxylic acid series of estrogens.
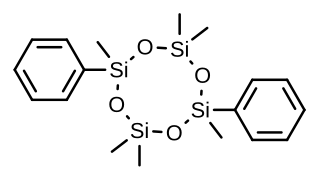
Quadrosilan is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen that was developed in the 1970s and that is or has been used as an antigonadotropic agent in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is an organosilicon compound, and is also known as 2,6-cisdiphenylhexamethylcyclotetrasiloxane. Quadrosilan has estrogenic activity equivalent to that of estradiol, and can produce feminization and gynecomastia as side effects in male patients.

Atrimustine, also known as bestrabucil or busramustine, is a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was under development in Japan by Kureha Chemicals for the treatment of breast cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma as well as for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease in bone marrow transplant recipients. It is the benzoate ester of an ester conjugate of estradiol and chlorambucil, which results in targeted/site-directed cytostatic activity toward estrogen receptor–positive tissues such as breast and bone. It reached preregistration for the treatment of cancer but was ultimately discontinued. Estrogenicic side effects of atrimustine in clinical trials included vaginal bleeding and gynecomastia. The drug was first patented in 1980.

Hexestrol diacetate (JAN) is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and was discovered in 1939.

Hexestrol dipropionate, or hexestrol dipropanoate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and has been known since at least 1931. The drug has been used in the past to inhibit lactation in women.
Hexestrol dicaprylate, or dioctanoylhexestrol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that is no longer marketed. It is a long-acting ester of hexestrol.

Diethylstilbestrol disulfate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that was formerly marketed but is now no longer available. It is described as an antineoplastic agent.

ICI-85966, also known as diethylstilbestrol (DES) bis(di carbamate), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent of the stilbestrol group and a nitrogen mustard ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer but was never marketed.
Phenestrol, or fenestrol, also known as hexestrol bis[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenylacetate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of hexestrol which was developed in the early 1960s for the treatment of hormone-dependent tumors but was never marketed.

Estradiol mustard, also known as estradiol 3,17β-bis(4- phenyl)acetate, is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a phenylacetic acid nitrogen mustard-coupled estrogen ester that was never marketed. It is selectively distributed into estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tissues such as ER-expressing tumors like those seen in breast and prostate cancers. For this reason, estradiol mustard and other cytostatic-linked estrogens like estramustine phosphate have reduced toxicity relative to non-linked nitrogen mustard cytostatic antineoplastic agents. However, they may stimulate breast tumor growth due to their inherent estrogenic activity and are said to be devoid of major therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer, although estramustine phosphate has been approved for and is used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Estramustine is an estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed. It is a carbamate derivative of estradiol and acts in part as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. Estramustine phosphate, the C17β phosphate ester of estramustine and a prodrug of estramustine, estromustine, estradiol, and estrone, is marketed and used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Panomifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group related to tamoxifen that was under development as an antineoplastic agent by Egis Pharmaceuticals and IVAX Drug Research Institute in the 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer, but it was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials before development was terminated. The drug was described in 1981.

Estrone methyl ether, or estrone 3-methyl ether, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ether – specifically, the C3 methyl ether of estrone – which was never marketed. It has been used to synthesize mestranol.
















