Cheminformatics refers to use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "in silico" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such in silico techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied.
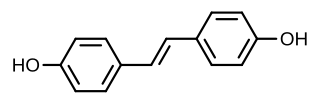
Stilbestrol, or stilboestrol, also known as 4,4'-dihydroxystilbene or 4,4'-stilbenediol, is a stilbenoid nonsteroidal estrogen and the parent compound of a group of more potent nonsteroidal estrogen derivatives that includes, most notably, diethylstilbestrol (DES). The term "stilbestrol" is often used incorrectly to refer to DES, but they are not the same compound.

Desoxycorticosterone acetate is a mineralocorticoid medication and a mineralocorticoid ester. It is formulated as an oil solution and is administered once daily by intramuscular injection. The medication is the C21 acetate ester of 11-deoxycorticosterone.
A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents.
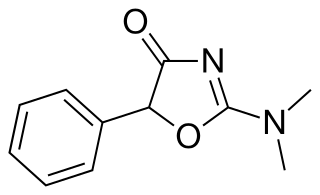
Thozalinone (USAN) is a psychostimulant that has been used as an antidepressant in Europe. It has also been trialed as an anorectic. Thozalinone is described as a "dopaminergic stimulant", and likely acts via inducing the release of dopamine and to a minimal extent norepinephrine; similar to analogue pemoline, it is seemingly devoid of abuse potential unlike common psychostimulants that increase catecholamines.

Trioxifene (INN), or as the salt trioxifene mesylate (USAN), is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with competitive binding activity against estradiol for the ERα and antagonistic activity against ERα-mediated gene expression, that was under preclinical and clinical development by Eli Lilly and Company for breast cancer and prostate cancer, but was abandoned. Its affinity for the rat estrogen receptor was reported to be 20% relative to estradiol.

Benzestrol is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group which was formerly used medically but has since been discontinued. The stilbestrol estrogens, the best-known of which is diethylstilbestrol (DES) were used extensively in the mid-1900s and were finally banned by the FDA due to them causing tumors in the children of women who used them.

Hexestrol, sold under the brand name Synestrol among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen which was previously used for estrogen replacement therapy and in the treatment of certain hormone-dependent cancers as well as gynecological disorders but is mostly no longer marketed. It has also been used in the form of esters such as hexestrol diacetate and hexestrol dipropionate. Hexestrol and its esters are taken by mouth, held under the tongue, or via injection into muscle.

Methestrol or methoestrol, also known as promethestrol or promethoestrol (BAN) or as dimethylhexestrol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol which is no longer marketed.
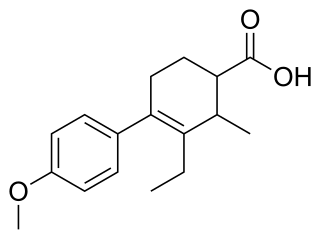
Carbestrol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the cyclohexenecarboxylic acid group and seco analogue of doisynolic acid that was described in the literature in 1956 and developed for the treatment of prostate cancer in the 1960s but was never marketed.

Hexestrol diacetate (JAN) is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and was discovered in 1939.

Hexestrol dipropionate, or hexestrol dipropanoate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and has been known since at least 1931. The drug has been used in the past to inhibit lactation in women.
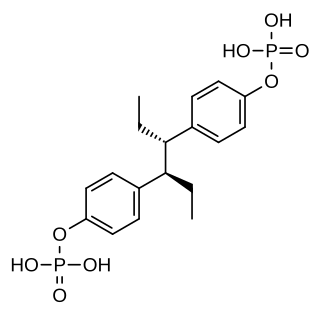
Hexestrol diphosphate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol and used as an estrogen and antineoplastic agent in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is a water-soluble ester of hexestrol. The medication has been known since at least 1956.

Dianol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. It is a dimer and impurity of anol, and was, along with hexestrol, involved in erroneous findings of highly potent estrogenic activity with anol. Although a potent estrogen, it requires a dose of 100 μg to show activity, whereas hexestrol shows activity with a mere dose of 0.2 μg.
Phenestrol, or fenestrol, also known as hexestrol bis[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenylacetate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of hexestrol which was developed in the early 1960s for the treatment of hormone-dependent tumors but was never marketed.

Acetryptine (INN), also known as 5-acetyltryptamine (5-AT), is a drug described as an antihypertensive agent which was never marketed. Structurally, acetryptine is a substituted tryptamine, and is closely related to other substituted tryptamines like serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). It was developed in the early 1960s. The binding of acetryptine to serotonin receptors does not seem to have been well-investigated, although it was assessed at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors and found to bind to them with high affinity. The drug may also act as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI); specifically, as an inhibitor of MAO-A.

Lilopristone (INN) is a synthetic, steroidal antiprogestogen with additional antiglucocorticoid activity which was developed by Schering and was patented in 1985. It is described as an abortifacient and endometrial contraceptive. The drug differs from mifepristone only in the structure of its C17α side chain, and is said to have much reduced antiglucocorticoid activity in comparison.
Prednazate, a combination of prednisolone hemisuccinate with perphenazine, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid as well as typical antipsychotic and sedative/tranquilizer. It was a component of Sixty Six-20, a combination of prednazate and chlorpheniramine.













