
Oligostilbenoids (oligo- or polystilbenes) are oligomeric forms of stilbenoids. Some molecules are large enough to be considered polyphenols and constitute a class of tannins. [1]

Oligostilbenoids (oligo- or polystilbenes) are oligomeric forms of stilbenoids. Some molecules are large enough to be considered polyphenols and constitute a class of tannins. [1]

Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids. The term tannin is widely applied to any large polyphenolic compound containing sufficient hydroxyls and other suitable groups to form strong complexes with various macromolecules.

Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene. They have a C6–C2–C6 structure. In biochemical terms, they belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with chalcones. Most stilbenoids are produced by plants, and the only known exception is the antimicrobial stilbenoid drug tapinarof which is biosynthesized by the Gram-negative bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens.

Emodin (6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is an organic compound. Classified as an anthraquinone, it can be isolated from rhubarb, buckthorn, and Japanese knotweed. Emodin is particularly abundant in the roots of the Chinese rhubarb, knotweed and knotgrass as well as Hawaii ‘au‘auko‘i cassia seeds or coffee weed. It is specifically isolated from Rheum palmatum L. It is also produced by many species of fungi, including members of the genera Aspergillus, Pyrenochaeta, and Pestalotiopsis, inter alia. The common name is derived from Rheum emodi, a taxonomic synonym of Rheum australe, and synonyms include emodol, frangula emodin, rheum emodin, 3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone, Schüttgelb (Schuttgelb), and Persian Berry Lake.
Shorea seminis is a species of tree in the family Dipterocarpaceae. It is native to Borneo and Palawan.

Dryobalanops aromatica, commonly known as Borneo camphor, camphor tree, Malay camphor, or Sumatran camphor, is a species of plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The species name aromatica is derived from Latin and refers to the smell of the dammar (resin). This species was one of the main sources of camphor and attracted early Arab traders to Borneo, at that time being worth more than gold, and used for incense and perfumes.

Acetogenins are a class of polyketide natural products found in plants of the family Annonaceae. They are characterized by linear 32- or 34-carbon chains containing oxygenated functional groups including hydroxyls, ketones, epoxides, tetrahydrofurans and tetrahydropyrans. They are often terminated with a lactone or butenolide. Over 400 members of this family of compounds have been isolated from 51 different species of plants. Many acetogenins are characterized by neurotoxicity.

Macaranga gigantea is a pioneer tree species from western Indo-China and Malesia including Sulawesi.
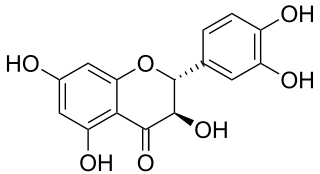
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols. It is extracted from plants such as Siberian larch and milk thistle.

Ampelopsin, also known as dihydromyricetin and DHM, when used as an effective ingredient in supplements and other tonics, is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It is extracted from the Japanese raisin tree and found in Ampelopsis species japonica, megalophylla, and grossedentata; Cercidiphyllum japonicum; Hovenia dulcis; Rhododendron cinnabarinum; some Pinus species; and some Cedrus species, as well as in Salix sachalinensis.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.

α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.

trans-Diptoindonesin B is an oligomeric stilbenoid.
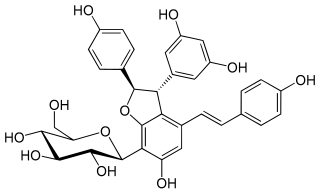
Diptoindonesin A is a C-glucoside of ε-viniferin isolated from the two Dipterocarpaceae Shorea seminis and Dryobalanops aromatica.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó or huáng bò is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.

Astringin is a stilbenoid, the 3-β-D-glucoside of piceatannol. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis and Picea abies.
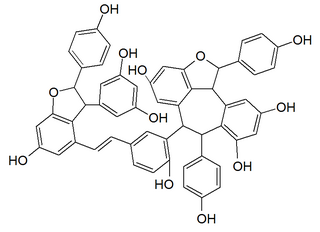
Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B.

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.

α-Cadinol or 10α-hydroxy-4-cadinene is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol.

The diarylheptanoids are a class of plant secondary metabolites. Diarylheptanoids consist of two aromatic rings joined by a seven carbons chain (heptane) and having various substituents. They can be classified into linear (curcuminoids) and cyclic diarylheptanoids. The best known member is curcumin, which is isolated from turmeric and is known as food coloring E100. Some other Curcuma species, such as Curcuma comosa also produce diarylheptanoids.
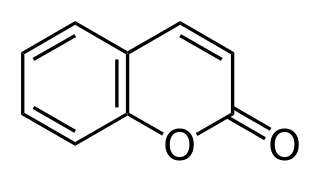
Coumarin derivatives are derivatives of coumarin and are considered phenylpropanoids. Among the most important derivatives are the 4-hydroxycoumarins, which exhibit anticoagulant properties, a characteristic not present for coumarin itself.