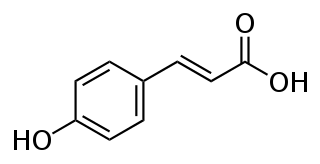
p-Coumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CH=CHCO2H. It is one of the three isomers of hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a white solid that is only slightly soluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.

Aiphanes horrida is a palm native to northern South America and Trinidad and Tobago. Aiphanes horrida is a solitary, spiny tree. In the wild it grows 3–10 metres tall tall with a stem diameter of 6–10 centimetres ; cultivated trees may be as much as 15 m (49') tall with a 15 cm (6") diameter. The epicarp and mesocarp of the fruit are rich in carotene and are eaten in Colombia, while the seeds are used to make candles. In parts of the Colombian Llanos endocarps are used to play games.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.

Piceatannol is a stilbenoid, a type of phenolic compound.

Ibudilast is an anti-inflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE4 subtype to the greatest extent, but also showing significant inhibition of other PDE subtypes.

Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) is a flavone, a type of flavonoid, originally isolated from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis and Scutellaria lateriflora. It is also reported in Oroxylum indicum and Thyme. It is the aglycone of baicalin. Baicalein is one of the active ingredients of Sho-Saiko-To, which is a Chinese classic herbal formula, and listed in Japan as Kampo medicine. As a Chinese herbal supplement, it is believed to enhance liver health.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó or huáng bò is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.

In molecular biology, mir-221 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
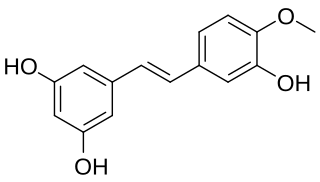
Rhapontigenin is a stilbenoid. It can be isolated from Vitis coignetiae or from Gnetum cleistostachyum.
In molecular biology mir-638 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-663 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

Stilbenolignans are phenolic compounds formed from a stilbenoid and a lignan.
Gnetum cleistostachyum is a liana species in the Sessiles subsection of the genus Gnetum described from South East Yunnan.

Isorhapontin is a stilbenoid. It is the glucoside of isorhapontigenin. It can be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces, in the bark of Picea sitchensis or in white spruce.
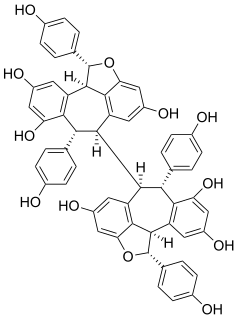
Oligostilbenoids are oligomeric forms of stilbenoids. Some molecules are large enough to be considered polyphenols and constitute a class of tannins.
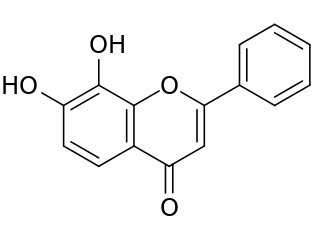
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

Li Jiayang is a Chinese agronomist and geneticist. He is Vice Minister of Agriculture in China and President of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS). He is also Professor and Principal investigator at the Institute of Genetics and Development at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
Kang Zhang is a Chinese-American ophthalmologist specializing in ophthalmic genetics and aging processes in the eye. He is currently a Professor of the Faculty of Medicine at Macau University of Science and Technology. He was previously a Professor of Ophthalmology and the Founding Director of the Institute for Genomic Medicine at the University of California, San Diego. Zhang is particularly known for his work on lanosterol, stem cell research, gene editing, and artificial intelligence.














