Contents
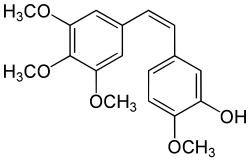 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methoxy-5-[(1Z)-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethen-1-yl]phenol | |
| Other names Combretastatin A4 CA-4 1-(3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl)-2-(3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxyphenyl)ethene 3,4,5-Trimethoxy-3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxystilbene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.159.667 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H20O5 | |
| Molar mass | 316.34 g/mol |
| Melting point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) [1] |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility in DMSO, Ethanol | DMSO : 63 mg/mL, Ethanol : 34 mg/mL [2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Combretastatin A-4 is a combretastatin and a stilbenoid. It can be isolated from Combretum afrum , the Eastern Cape South African bushwillow tree or in Combretum leprosum , the mofumbo, a species found in Brazil. [3] [4]