 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
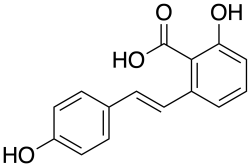
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-6-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethen-1-yl]benzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 256.257 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Hydrangeic acid is a stilbenoid found in the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla . [1]
Hydrangeic acid is being investigated as a possible antidiabetic drug as it significantly lowered blood glucose, triglyceride and free fatty acid levels in laboratory animals. [1]