
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the Curcuma longa species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric, a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetics ingredient, food flavoring, and food coloring.

Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula or C6H5CH=CHCHO. Occurring naturally as predominantly the trans (E) isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. This pale yellow, viscous liquid occurs in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum. The essential oil of cinnamon bark is about 90% cinnamaldehyde. Cinnamaldehyde decomposes to styrene because of oxidation as a result of bad storage or transport conditions. Styrene especially forms in high humidity and high temperatures. This is the reason why cinnamon contains small amounts of styrene.

Cinnamic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5-CH=CH-COOH. It is a white crystalline compound that is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many organic solvents. Classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, it occurs naturally in a number of plants. It exists as both a cis and a trans isomer, although the latter is more common.

Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized de novo by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids, and alkaloids; however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection.

Rutin is the glycoside combining the flavonol quercetin and the disaccharide rutinose. It is a flavonoid glycoside found in a wide variety of plants, including citrus.

Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene. They have a C6–C2–C6 structure. In biochemical terms, they belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with chalcones. Most stilbenoids are produced by plants, and the only known exception is the antihelminthic and antimicrobial stilbenoid, 2-isopropyl-5-[(E)-2-phenylvinyl]benzene-1,3-diol, biosynthesized by the Gram-negative bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens.
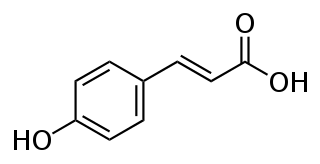
p-Coumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CH=CHCO2H. It is one of the three isomers of hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a white solid that is only slightly soluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.

The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid.

Piceatannol is the organic compound with the formula ( 2C6H3)2CH)2. Classified as a stilbenoid and a phenol, it is a white solid, although samples often are yellow owing to impurities.

The enzyme phenylalanine ammonia lyase (EC 4.3.1.24) catalyzes the conversion of L-phenylalanine to ammonia and trans-cinnamic acid.:
In enzymology, a pinosylvin synthase (EC 2.3.1.146) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Olivetol, also known as 5-pentylresorcinol or 5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol, is an organic compound found in certain species of lichen; it is also a precursor in various syntheses of tetrahydrocannabinol.

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.
The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes.

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.
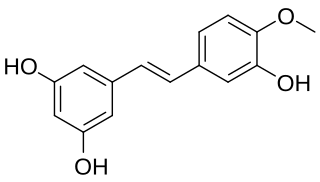
Rhapontigenin is a stilbenoid. It can be isolated from Vitis coignetiae or from Gnetum cleistostachyum.

Isorhapontigenin is a tetrahydroxylated stilbenoid with a methoxy group. It is an isomer of rhapontigenin and an analog of resveratrol. It is found in the Chinese herb Gnetum cleistostachyum, in Gnetum parvifolium and in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.
Gnetum cleistostachyum is a liana species in the Sessiles subsection of the genus Gnetum described from South East Yunnan.

Pisatin (3-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4′,5′-methylenedioxy-chromanocoumarane) is the major phytoalexin made by the pea plant Pisum sativum. It was the first phytoalexin to be purified and chemically identified. The molecular formula is C17H14O6.

















