
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis. Grapes are a non-climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.

The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines and Virginia creeper. The family name is derived from the genus Vitis.

Vaccinium vitis-idaea is a small evergreen shrub in the heath family Ericaceae, known colloquially as the lingonberry, partridgeberry, foxberry, mountain cranberry, or cowberry. It is native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Northern Hemisphere, including Eurasia and North America. Commercially cultivated in the United States Pacific Northwest and the Netherlands, the edible berries are also picked in the wild and used in various dishes, especially in Nordic cuisine.
Beta is a winter-hardy variety of North American grape derived from a cross of the Vitis labrusca-based cultivar Concord and a selection of Vitis riparia, the wild riverbank grape, called Carver. It is an extremely cold-hardy grape that is self-fertile. This variety is grown successfully in Finland and was widely planted in Minnesota in the early 20th century. It ripens in late September in New York State. It bears dark, blue-black fruit that is used for jellies, fruit juices, etc., but rarely for wine.

Viti Levu is the largest island in Fiji. It is the site of the country's capital and largest city, Suva, and home to a large majority of Fiji's population.

Vitis labrusca, the fox grape, is a species of grapevines belonging to the Vitis genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to eastern North America and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba, Concord, Delaware, Isabella, Niagara, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam, Alexander and Onaka. Among the characteristics of this vine species in contrast to the European wine grape Vitis vinifera are its "slip-skin" that allows the skin of the grape berries to easily slip off when squeezed, instead of crushing the pulp, and the presence of tendrils on every node of the cane. Another contrast with European vinifera is the characteristic "foxy" musk of V. labrusca, best known to most people through the Concord grape. This musk is not related to the mammalian fox, but rather to the strong, earthy aromas characteristic of the grapes that were known by early European-American settlers in the New World. The term "foxy" became a sort of catchall for the wine tasting descriptors used for these American wines that were distinct from the familiar flavors of the European viniferous wines.

Mauritia flexuosa, known as the moriche palm, ité palm, ita, buriti, muriti, miriti (Brazil), canangucho (Colombia), morete or acho (Ecuador), or aguaje (Peru), is a palm tree. It grows in and near swamps and other wet areas in tropical South America.

Agonis flexuosa, commonly known as peppermint, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. The Noongar peoples know the tree as wanil, wonnow, wonong or wannang. It is a tree or shrub with pendulous, very narrowly elliptic, narrowly elliptic or narrowly egg-shaped leaves, white flowers with 20 to 25 stamens opposite the sepals and broadly top-shaped to broadly cup-shaped capsules.

Hybrid grapes are grape varieties that are the product of a crossing of two or more Vitis species. This is in contrast to crossings between grape varieties of the same species, typically Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine. Hybrid grapes are also referred to as inter-species crossings or "Modern Varieties." Due to their often excellent tolerance to powdery mildew, other fungal diseases, nematodes, and phylloxera, hybrid varieties have, to some extent, become a renewed focus for European breeding programs. The recently developed varieties are examples of newer hybrid grape varieties for European viticulturalists. Several North American breeding programs, such as those at Cornell and the University of Minnesota, focus exclusively on hybrid grapes, with active and successful programs, having created hundreds if not thousands of new varieties.

Vitis (grapevine) is a genus of 81 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus consists of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture.

Deschampsia flexuosa, commonly known as wavy hair-grass, is a species of bunchgrass in the grass family widely distributed in Eurasia, Africa, South America, and North America.

Neuropteris is an extinct seed fern that existed in the Carboniferous period, known only from fossils.

Vitis flexuosa is a species of liana in the grape family.

Vitis bryoniifolia is a prolific and adaptable, polygamo-dioecious species of climbing vine in the grape family native to China, where it is known as ying yu(Traditional Chinese: 蘡薁 Simplified Chinese: 蘡薁), or hua bei pu tao. The variant form ternata is known as san chu ying yu (Traditional and Simplified Chinese: 三出蘡薁), meaning Three-Spiked-Leafed Ying Yu.
Vitis chunganensis is a species of climbing vine in the grape family native to China. In Chinese it is called dong nan pu tao, or Southeast grape.
Flexuosa, meaning "full of bends" in Latin, may refer to:
Antispila ampelopsia is a moth of the family Heliozelidae. It was described by Kuroko in 1961. It is found in Japan.

Oligostilbenoids are oligomeric forms of stilbenoids. Some molecules are large enough to be considered polyphenols and constitute a class of tannins.
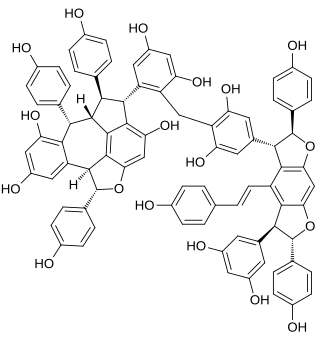
Chunganenol is a resveratrol hexamer found in Vitis chunganensis.















