A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis.

Vitis amurensis, the Amur grape, is a species of grape native to the Asian continent. Its name comes from the Amur Valley in Russia and China.

Hybrid grapes are grape varieties that are the product of a crossing of two or more Vitis species. This is in contrast to crossings between grape varieties of the same species, typically Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine. Hybrid grapes are also referred to as inter-specific crossings or "Modern Varieties." Due to their often excellent tolerance to powdery mildew, other fungal diseases, nematodes, and phylloxera, hybrid varieties have, to some extent, become a renewed focus for European breeding programs. The recently developed varieties, Rondo, and Regent are examples of newer hybrid grape varieties for European viticulturalists. Several North American breeding programs, such as those at Cornell and the University of Minnesota, focus exclusively on hybrid grapes, with active and successful programs, having created hundreds if not thousands of new varieties.

Rondo is a dark-skinned grape variety, used for making red wine. It is a hybrid grape or inter-specific crossing. It was created in 1964 by Professor Vilém Kraus in then-Czechoslovakia by crossing the varieties Zarya Severa and St. Laurent. He offered it to Dr. Helmut Becker (1927-1990) of the Geisenheim Grape Breeding Institute who conducted further work on it, which explains why the grape is known under a Geisenheim designation. The variety was first planted for research and later in bigger scale in the mid 1980s by Thomas Walk Vineyard in Ireland under the name Amurensis Walk; it was named Rondo in 1997.

Vitis (grapevines) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture.
Severny is the name of a Russian red-grape variety. Severny results from the interspecific crossing between Seianetze Malengra and Vitis amurensis. The hybrid has been obtained in the Institute for wineyard researches in Rostov-on-Don in Russia. The variety has been imported to Finger Lakes AVA, just south of Lake Ontario, in the United States.

Bronner is a white grape variety used for wine. It was bred in 1975 by Norbert Becker at the viticultural institute in Freiburg, Germany. The variety was initially known under its breeding code FR 250-75, and was later named in honour of Johann Philipp Bronner (1792-1864), who was a German pharmacist and viticultural pioneer. It received varietal protection in 1977.

Theretra japonica is a moth of the family Sphingidae first described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1869.

Deilephila askoldensis is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is found in southeastern Russia, northeastern China, the Korean Peninsula, and northern Japan. D. askoldensis has a wingspan of 51–59 mm. Larvae feed on Vitis amurensis in Russia and Epilobium species in Japan.

Retusin is an O-methylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Fabaceae species like Dipteryx odorata, in Dalbergia retusa and in Millettia nitida. It can also be found in Maackia amurensis cell cultures.
Vitis acerifolia is a species of grape native to the south-central part of the Great Plains of the United States. Its leaf shape is the origin of its name, which is Latin for maple-leaf grape, but it is widely referenced in literature by the synonym, Vitis longii.
Phyllocnistis vitella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae, known from Russia. The hostplant for the species is Vitis amurensis.

Sphecodina caudata is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is found in the southern Russian Far East, the Korean Peninsula, eastern and southern China and northern Thailand.

Rhagastis mongoliana is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is found from China, north to Mongolia, Korea and the Primorsky Krai in Russia, and east to Taiwan and Japan.

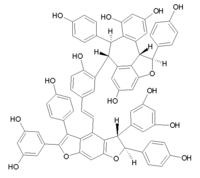
Amurensin K is an oligostilbene. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis amurensis. Preliminary tests have shown it to be an effective neuraminidase inhibitor against the influenza A virus subtype H1N1.
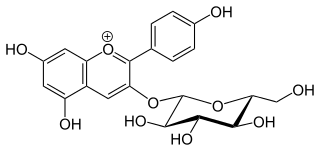
Callistephin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-O-glucoside of pelargonidin.

Amurensin A is an oligostilbene isolated from the roots of Vitis amurensis. It is a partially oxidized resveratrol dimer with a C8-C8' connection.

Cyphostemmin A is an oligostilbene found in Cyphostemma crotalarioides (Vitaceae).
Zarya severa is a red grape variety. It is a descendant of the Asiatic wild grape Vitis amurensis and the grape Malingre Précoce and is thus a hybrid vine. The crossing took place at the Potapenko Viticulture Research Institute in Rostov Oblast, Russia in 1936. Because of its high winter frost resistance as well as its resistance to downy mildew, this variety, often mentioned by breeders in Eastern Europe, became a major breeding stock in the search for new varieties.