
The Vitaceae are a family of flowering plants, with 14 genera and around 910 known species, including common plants such as grapevines and Virginia creeper. The family name is derived from the genus Vitis.

Cissus is a genus of approximately 350 species of lianas in the grape family (Vitaceae). They have a cosmopolitan distribution, though the majority are to be found in the tropics.

Cyphostemma is a flowering plant genus in the family Vitaceae, with around 250 species distributed throughout the tropics and subtropics. These species are caudiciform and used to belong to the genus Cissus. The genus name comes from Greek kyphos, meaning hump, and stemma, meaning garland.

Tetrastigma is a genus of plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. The plants are lianas that climb with tendrils and have palmately compound leaves. Plants are dioecious, with separate male and female plants; female flowers are characterized by their four-lobed stigmas. The species are found in subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, Malaysia, and Australia, where they grow in primary rainforest, gallery forest and monsoon forest and moister woodland. Species of this genus are notable as being the sole hosts of parasitic plants in the family Rafflesiaceae, one of which, Rafflesia arnoldii, produces the largest single flower in the world. Tetrastigma is the donor species for horizontal gene transfer to Sapria and Rafflesia due to multiple gene theft events.

The genus Cayratia consists of species of vine plants, typical of the tribe Cayratieae. Some of them are useful, and they are found in tropical and subtropical areas of Asia, Africa, Australia, and islands of the Pacific Ocean.

Pachycauls are plants with a disproportionately thick trunk for their height, and few branches. In contrast, trees with thin twigs such as Oak (Quercus), Maple (Acer) and Eucalyptus are called leptocauls while those with moderately thick twigs like Plumeria are called mesocauls. Pachycauly can be the product of exceptional primary growth or disproportionate secondary growth as with the Baobabs (Adansonia). The word is derived from the Greek pachy- meaning thick or stout, and Latin caulis meaning the stem. All of the tree species of cactus are pachycauls, as are most palms, Cycads and pandans. The most extreme pachycauls are the floodplains, or riverbottom variety of the African Palmyra with primary growth up to seven feet in thickness, and the Coquito Palm with primary growth up to six feet thick. The most pachycaulous cycad is Cycas thouarsii at up to five feet in diameter. The tallest pachycaul is the Andean Wax Palm at up to 220 feet. and about 16 inches (41 cm) in diameter. The most pachycaulous cactus is the Bisnaga with primary growth up to 4 ft 4 in in diameter. The largest caudex type pachycaul is the African Baobab. One called the Glencoe Baobab at Hoedspruit, South Africa has a basal diameter of 52 ft 2 in. This tree suffered a severe trauma and is dying.

Cyphostemma currorii is a succulent tree belonging to the family Vitaceae, also known as Koba or Butter-tree. They grow and reach a height of 6 meters or more. Cyphostemma currorii is found in hot, arid rocky places, and has been seen from southern Angola to Namibia and is common on the Brandberg.
Hopea malibato is a species of plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. It is endemic to the Philippines.
The molecular formula C28H22O6 (molar mass: 454.47 g/mol, exact mass: 454.141638 u) may refer to :

trans-Diptoindonesin B is an oligomeric stilbenoid.

Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).

Ampelopsin B is a stilbenoid dimer found in Ampelopsis glandulosa var. hancei.

Amurensin K is an oligostilbene. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis amurensis. Preliminary tests have shown it to be an effective neuraminidase inhibitor against the influenza A virus subtype H1N1.
Cyphostemma crotalarioides is a flowering plant species in the genus Cyphostemma found in Burkina Faso.
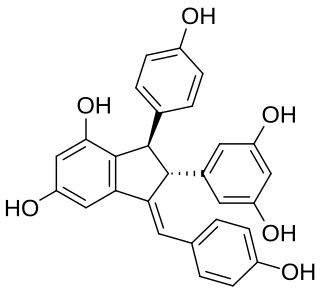
Cyphostemmin B is an oligostilbene found in Cyphostemma crotalarioides (Vitaceae). It is a resveratrol dimer.

Cyphostemma mappia is a species of caudiciform succulent plant endemic to Mauritius. It is sometimes known as the "Mauritian baobab", though it is member of the grape family (Vitaceae) and unrelated to the true Baobabs of Africa.

Gordon Douglas Rowley (1921–2019) was a British botanist and writer specialising in cacti and succulents.

The Cayratieae is one of five tribes of vine plants that are now recognised in this subfamily Vitoideae. It contains genera restored or newly erected from species in the previously configured genus Cayratia, which was found not be monophyletic:.














