
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol or polyphenol and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts.
A tetrameric protein is a protein with a quaternary structure of four subunits (tetrameric). Homotetramers have four identical subunits, and heterotetramers are complexes of different subunits. A tetramer can be assembled as dimer of dimers with two homodimer subunits, or two heterodimer subunits.

Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene. They have a C6–C2–C6 structure. In biochemical terms, they belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with chalcones. Most stilbenoids are produced by plants, and the only known exception is the antimicrobial stilbenoid drug tapinarof which is biosynthesized by the Gram-negative bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.

Phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—occur naturally in wine. These include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.
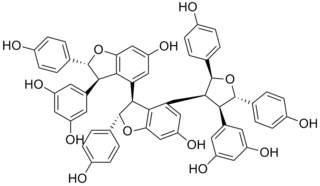
Kobophenol A is a stilbenoid. It is a tetramer of resveratrol. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu, from Caragana sinica and from Carex folliculata seeds.

A tetramer (tetra-, "four" + -mer, "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called tetramery. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula Ti(OCH3)4, which is tetrameric in solid state and has the molecular formula Ti4(OCH3)16. An example from organic chemistry is kobophenol A, a substance that is formed by combining four molecules of resveratrol.
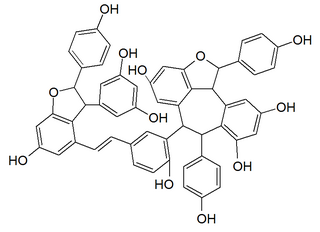
Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B.

Vitisin A is a natural phenol found in red wines. It is a pyranoanthocyanin.

Vitisin B is a natural phenol found in red wines. It is a pyranoanthocyanin.

Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).

Parthenocissus laetevirens is a climbing plant species in the genus Parthenocissus found in China.

Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae like Shorea ovalis. It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.

Flexuosol A is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis flexuosa.

Amurensin K is an oligostilbene. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in Vitis amurensis. Preliminary tests have shown it to be an effective neuraminidase inhibitor against the influenza A virus subtype H1N1.

Isorhapontigenin is a tetrahydroxylated stilbenoid with a methoxy group. It is an isomer of rhapontigenin and an analog of resveratrol. It is found in the Chinese herb Gnetum cleistostachyum, in Gnetum parvifolium and in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.

Oligostilbenoids are oligomeric forms of stilbenoids. Some molecules are large enough to be considered polyphenols and constitute a class of tannins.














