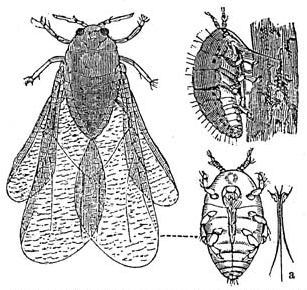
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera ; originally described in France as Phylloxera vastatrix; equated to the previously described Daktulosphaera vitifoliae, Phylloxera vitifoliae. The insect is commonly just called phylloxera.

Aurore is a white complex hybrid grape variety produced by Albert Seibel and used for wine production mostly in the United States and Canada. Over a long lifetime Seibel produced many complex hybrid crosses of Vitis vinifera to American grapes. It is a cross of Seibel 788 and Seibel 29.

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.

Agawam is a hybrid grape variety. It is a crossing of Carter and Muscat Hamburg. Agawam is one of the so-called Rogers' Hybrids created by E.S. Rogers in the early-to-mid-19th century, and is unique among the named cultivars of that group in that it is self-fertile.
Vitis labrusca, the fox grape, is a species of grapevines belonging to the Vitis genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to eastern North America and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba, Concord, Delaware, Isabella, Niagara, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam, Alexander and Onaka. Among the characteristics of this vine species in contrast to the European wine grape Vitis vinifera are its "slip-skin" that allows the skin of the grape berries to easily slip off when squeezed, instead of crushing the pulp, and the presence of tendrils on every node of the cane. Another contrast with European vinifera is the characteristic "foxy" musk of V. labrusca, best known to most people through the Concord grape. This musk is not related to the mammalian fox, but rather to the strong, earthy aromas characteristic of the grapes that were known by early European-American settlers in the New World. The term "foxy" became a sort of catchall for the wine tasting descriptors used for these American wines that were distinct from the familiar flavors of the European viniferous wines.

Vitis rupestris is a species of grape native to the United States that is known by many common names including July, Coon, sand, sugar, beach, bush, currant, ingar, rock, and mountain grape. It is used for breeding several French-American hybrids as well as many root stocks.
Vitis × labruscana is a subgroup of grapes originating from a hybridization of Vitis labrusca and Vitis vinifera. Popular examples include Concord and Niagara grapes, which comprise nearly all grapes processed for juice or jelly in the United States. Such cultivars are frequently referred to as "labrusca", however many are as little as half Vitis labrusca in their pedigree. Another common term, arguably more accurate, is "labrusca-type". These varieties do in fact possess many of the traits of Vitis labrusca, frequently including slipskin fruit, strong "foxy" flavor/odor, and large leaves with lighter colored and pubescent undersides. Most are self-fertile, unlike wild Vitis labrusca.

Hybrid grapes are grape varieties that are the product of a crossing of two or more Vitis species. This is in contrast to crossings between grape varieties of the same species, typically Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine. Hybrid grapes are also referred to as inter-specific crossings or "Modern Varieties." Due to their often excellent tolerance to powdery mildew, other fungal diseases, nematodes, and phylloxera, hybrid varieties have, to some extent, become a renewed focus for European breeding programs. The recently developed varieties, Rondo, and Regent are examples of newer hybrid grape varieties for European viticulturalists. Several North American breeding programs, such as those at Cornell and the University of Minnesota, focus exclusively on hybrid grapes, with active and successful programs, having created hundreds if not thousands of new varieties.

Vitis (grapevines) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture.

Solaris is a variety of grape used for white wine. It was created in 1975 at the grape breeding institute in Freiburg, Germany by Norbert Becker.

Vitis berlandieri is a species of grape native to the southern North America, primarily Texas, New Mexico and Arkansas.
Vinifera is a locality in Victoria, Australia, located approximately 22 km from Swan Hill, Victoria. It was named after Vitis vinifera the Common Grape Vine, when grapes were planted here on irrigated land. As of the 2016 census, Vinifera has a population of 159.
Flora is the name of two unrelated varieties of grape, one white and one red, both of United States origin.
Black Spanish was originally assumed to be a seedling of an American hybrid grape which resulted from a crossing of the American Vitis aestivalis species of grape with an unknown Vitis vinifera pollen donor. However, just recently it has been revealed from microsatellite DNA analysis, that the American wild grapevine parent of Black Spanish is Vitis berlandieri and not Vitis aestivalis. This hybridization is not known to have been purposeful, and may have occurred naturally, as was the case with many of the early American grape cultivars. Riaz et al. (2019) have now published the genetic profile of the Jacquez grapevine as follows (percentages): V. vinifera: 69% V. berlandieri: 21% V. rupestris: 7% V. riparia: 3%.
Vitis silvestrii is a species of polygamo-dioecious plant in the grape family native to the forested slopes of western Hubei and southern Shaanxi in China from 300 to 1200 meters above sea level. Its flowers appear in May, males having abortive pistils

Olmo grapes are wine and table grape varieties produced by University of California, Davis viticulturist Dr. Harold Olmo. Over the course of his nearly 50-year career, Dr. Olmo bred a wide variety of both grapes by means of both crossing varieties from the same species or creating hybrid grapes from cultivars of different Vitis species.

Vitisin C is a hydroxystilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus Vitis (grapevines).

L'Acadie blanc is a white Canadian wine grape variety that is a hybrid crossing of Cascade and Seyve-Villard 14-287. The grape was created in 1953 by grape breeder Ollie A. Bradt in Niagara, Ontario at the Vineland Horticultural Research Station which is now the Vineland Research and Innovation Centre. Today the grape is widely planted in Nova Scotia with some plantings in Quebec and Ontario. Some wine writers, including those at Appellation America, consider L'Acadie blanc as "Nova Scotia’s equivalent to Chardonnay".













