
Fosfestrol, sold under the brand name Honvan and also known as diethylstilbestrol diphosphate (DESDP), is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is given by slow intravenous infusion once per day to once per week or by mouth once per day.

Dienestrol, also known as dienoestrol (BAN), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group which is or was used to treat menopausal symptoms in the United States and Europe. It has been studied for use by rectal administration in the treatment of prostate cancer in men as well. The medication was introduced in the U.S. in 1947 by Schering as Synestrol and in France in 1948 as Cycladiene. Dienestrol is a close analogue of diethylstilbestrol. It has approximately 223% and 404% of the affinity of estradiol at the ERα and ERβ, respectively.

Chlorotrianisene (CTA), also known as tri-p-anisylchloroethylene (TACE) and sold under the brand name Tace among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen related to diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was previously used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency in women and prostate cancer in men, among other indications, but has since been discontinued and is now no longer available. It is taken by mouth.

Acefluranol, also known as 2,3-bis(3,4-diacetoxy-5-fluorophenyl)pentane, is a nonsteroidal antiestrogen of the stilbestrol group that was never marketed. It is a polyfluorinated biphenyl that is related to polybrominated and polychlorinated biphenyls and diethylstilbestrol.

Paroxypropione, also known as paraoxypropiophenone, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which has been used medically as an antigonadotropin in Spain and Italy but appears to no longer be marketed. It was first synthesized in 1902. The antigonadotropic properties of the drug were discovered in 1951 and it entered clinical use shortly thereafter.
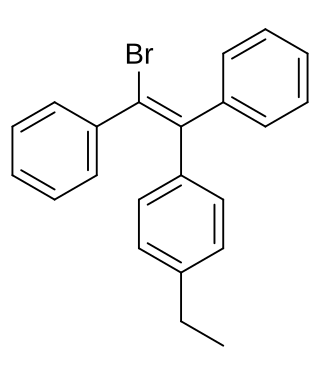
Broparestrol (INN), also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, orally active estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, the levorotatory isomer of which is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate (BANM), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid, and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol. The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.

Bifluranol is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that has been used as an antiandrogen in the United Kingdom in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is a polyfluorinated biphenyl that is related to polybrominated and polychlorinated biphenyls and diethylstilbestrol. The drug is described as a weak estrogen, and possesses about one-eighth the potency of diethylstilbestrol.
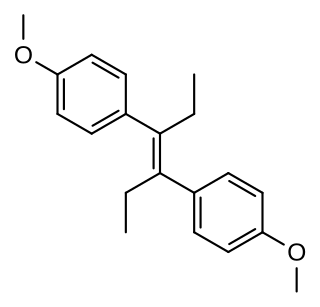
Dimestrol, also known as dianisylhexene, 4,4'-dimethoxy-α,α'-diethylstilbene, diethylstilbestrol dimethyl ether, and dimethoxydiethylstilbestrol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group which is related to diethylstilbestrol. It has been used clinically as a hormonal therapy in cases of delayed female puberty, hypogonadism, menopausal, and postmenopausal symptoms. It is known to induce the development of female secondary sexual characteristics in the case of female delayed puberty or hypogonadism. The drug has also been used as a growth promoter in livestock.

Hexestrol dipropionate, or hexestrol dipropanoate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and has been known since at least 1931. The drug has been used in the past to inhibit lactation in women.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diesthylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.

Bisdehydrodoisynolic acid (BDDA), as the (Z)-isomer ( -BDDA), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen related to doisynolic acid that was never marketed. It is one of the most potent estrogens known, although it has more recently been characterized as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). BDDA and other doisynolic acid derivatives display relatively low affinity accompanied by disproportionately high estrogenic potency in vivo, which was eventually determined to be due to transformation into metabolites with greater estrogenic activity. The drug was discovered in 1947 as a degradation product of the reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide. It is the seco-analogue of equilenin, while doisynolic acid is the seco-analogue of estrone. These compounds, along with diethylstilbestrol, can be considered to be open-ring analogues of estradiol. The methyl ether of BDDA, doisynoestrol, is also an estrogen, and in contrast to BDDA, has been marketed.

Mestilbol, also known as diethylstilbestrol monomethyl ether, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It was developed by Wallace & Tiernan Company, patented in 1940, and introduced for medical use in the 1940s, but is now no longer marketed. Mestilbol was available both as oral tablets and in oil for intramuscular injection. The drug is gradually demethylated in the body into diethylstilbestrol and hence is a prodrug of diethylstilbestrol. Mestilbol is a highly active estrogen, although somewhat less so than diethylstilbestrol, but is longer-lasting in comparison.
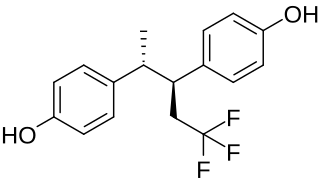
Terfluranol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was developed for the treatment of breast cancer but was never marketed. It was described in the medical literature in 1974.
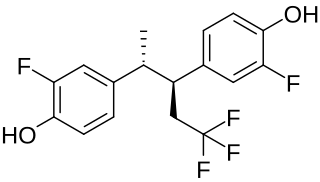
Pentafluranol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was developed for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia never marketed. It was described in the medical literature in 1974.
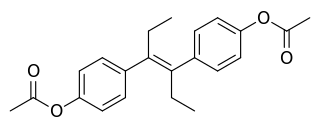
Diethylstilbestrol diacetate (DESDA) is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that was introduced for clinical use in the 1940s and was formerly marketed but is now no longer available.
Diethylstilbestrol dilaurate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that was previously marketed but is now no longer available. It was formulated and used as a micronized topical medication to treat acne in adolescent boys and young men. The drug was marketed as early as 1951.
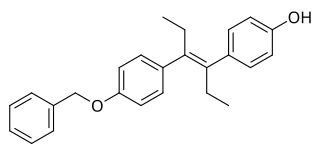
Diethylstilbestrol monobenzyl ether, also known as benzelstilbestrol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ether of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that is described as a pituitary gland inhibitor (antigonadotropin) and was formerly marketed but is now no longer available. It was first synthesized by Wallace & Tiernan Company in 1952, and was described by them as having only weak estrogenic activity. The drug was used to treat gynecological conditions and infertility in women.

ICI-85966, also known as diethylstilbestrol (DES) bis(di carbamate), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent of the stilbestrol group and a nitrogen mustard ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer but was never marketed.



















