
Fosfestrol, sold under the brand name Honvan and also known as diethylstilbestrol diphosphate (DESDP), is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is given by slow intravenous infusion once per day to once per week or by mouth once per day.

Chlorotrianisene (CTA), also known as tri-p-anisylchloroethylene (TACE) and sold under the brand name Tace among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen related to diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was previously used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency in women and prostate cancer in men, among other indications, but has since been discontinued and is now no longer available. It is taken by mouth.

Benzestrol is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group which was formerly used medically but has since been discontinued. The stilbestrol estrogens, the best-known of which is diethylstilbestrol (DES) were used extensively in the mid-1900s and were finally banned by the FDA due to them causing tumors in the children of women who used them.

Anol, also known as p-hydroxypropenylbenzene, is a simple phenol that was derived via demethylation from anethole, an estrogenic constituent of anise and fennel, by Sir Charles Dodds in 1937. It was reported to possess extremely potent estrogenic activity on par with that of steroidal estrogens like estrone, with a dose of 1 μg inducing estrus in rats. However, subsequent studies with different preparations of anol failed to confirm these findings, and it was found that dimerization of anol into dianol and hexestrol can rapidly occur and that the latter impurity was responsible for the highly potent estrogenic effects. Dodds later synthesized the structurally related and extremely potent estrogen diethylstilbestrol in 1938.

Hexestrol, sold under the brand name Synestrol among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen which was previously used for estrogen replacement therapy and in the treatment of certain hormone-dependent cancers as well as gynecological disorders but is mostly no longer marketed. It has also been used in the form of esters such as hexestrol diacetate and hexestrol dipropionate. Hexestrol and its esters are taken by mouth, held under the tongue, or via injection into muscle.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, orally active, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, whose levorotatory isomer is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid, and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol. The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.
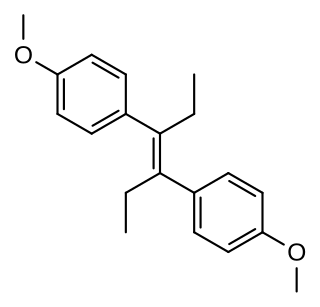
Dimestrol, also known as dianisylhexene, 4,4'-dimethoxy-α,α'-diethylstilbene, diethylstilbestrol dimethyl ether, and dimethoxydiethylstilbestrol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group which is related to diethylstilbestrol. It has been used clinically as a hormonal therapy in cases of delayed female puberty, hypogonadism, menopausal, and postmenopausal symptoms. It is known to induce the development of female secondary sexual characteristics in the case of female delayed puberty or hypogonadism. The drug has also been used as a growth promoter in livestock.

Hexestrol diacetate (JAN) is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and was discovered in 1939.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diethylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol, that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.

Ethinylestriol (EE3), or 17α-ethynylestriol, also known as 17α-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol, is a synthetic estrogen which was never marketed. Nilestriol, the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison, but, in contrast to ethinylestriol, has been marketed. Ethinylestriol has been found to reduce the risk of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary cancer when given as a prophylactic in animal models, while other estrogens like ethinylestradiol and diethylstilbestrol were ineffective.

Dianol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. It is a dimer and impurity of anol, and was, along with hexestrol, involved in erroneous findings of highly potent estrogenic activity with anol. Although a potent estrogen, it requires a dose of 100 μg to show activity, whereas hexestrol shows activity with a mere dose of 0.2 μg.

Mestilbol, also known as diethylstilbestrol monomethyl ether, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It was developed by Wallace & Tiernan Company, patented in 1940, and introduced for medical use in the 1940s, but is now no longer marketed. Mestilbol was available both as oral tablets and in oil for intramuscular injection. The drug is gradually demethylated in the body into diethylstilbestrol and hence is a prodrug of diethylstilbestrol. Mestilbol is a highly active estrogen, although somewhat less so than diethylstilbestrol, but is longer-lasting in comparison.
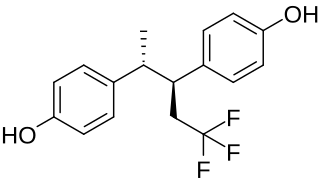
Terfluranol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was developed for the treatment of breast cancer but was never marketed. It was described in the medical literature in 1974.
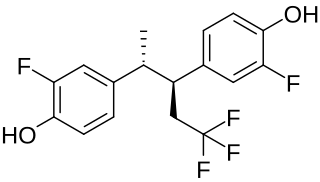
Pentafluranol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that was developed for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia never marketed. It was described in the medical literature in 1974.
Diethylstilbestrol dilaurate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that was previously marketed but is now no longer available. It was formulated and used as a micronized topical medication to treat acne in adolescent boys and young men. The drug was marketed as early as 1951.
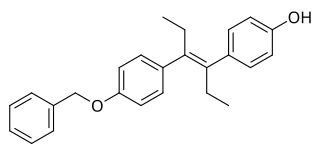
Diethylstilbestrol monobenzyl ether, also known as benzelstilbestrol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ether of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that is described as a pituitary gland inhibitor (antigonadotropin) and was formerly marketed but is now no longer available. It was first synthesized by Wallace & Tiernan Company in 1952, and was described by them as having only weak estrogenic activity. The drug was used to treat gynecological conditions and infertility in women.

Diethylstilbestrol disulfate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group and an ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) that was formerly marketed but is now no longer available. It is described as an antineoplastic agent.

ICI-85966, also known as diethylstilbestrol (DES) bis(di carbamate), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent of the stilbestrol group and a nitrogen mustard ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer but was never marketed.
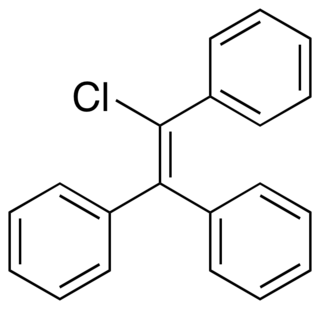
Triphenylchloroethylene, or triphenylchlorethylene, also known as chlorotriphenylethylene or as phenylstilbene chloride, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was marketed in the 1940s for the treatment of menopausal symptoms, vaginal atrophy, lactation suppression, and all other estrogen-indicated conditions.



















