The molecular formula C27H31O15+ (molar mass: 595.53 g/mol, exact mass: 595.1663 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C27H31O15+ (molar mass: 595.53 g/mol, exact mass: 595.1663 u) may refer to:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
The molecular formula C21H23NO5 (molar mass: 369.41 g/mol, exact mass: 369.1576 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H8O7 (molar mass: 192.12 g/mol, exact mass: 192.0270 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula BaSO4 (molar mass: 233.39 g/mol, exact mass: 233.8570 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.07825 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C9H13NO3 (molar mass: 183.20 g/mol, exact mass: 183.089543) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H9N3 (molar mass: 111.15 g/mol, exact mass: 111.0796 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H11NO2S (molar mass: 149.21 g/mol, exact mass: 149.0510 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H10O7 (molar mass: 194.14 g/mol, exact mass: 194.0427 u) may refer to:
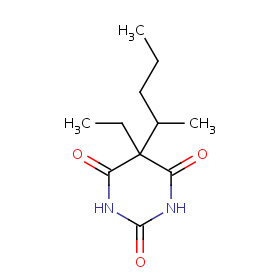
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C14H12O3 (molar mass: 228.25 g/mol, exact mass: 228.078644 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C8H16 (molar mass: 112.21 g/mol, exact mass: 112.1252 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C16H13O7 (or C16H13O7+, molar mass : 317.27 g/mol, exact mass : 317.066127317) or C16H13ClO7 (exact mass : 352.03498) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H11O6 (C15H11O6+, molar mass: 287.24 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0555626 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H25N3O (molar mass: 263.38 g/mol, exact mass: 263.1998 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H18BrNO2 (molar mass: 288.18 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0521 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C23H25O12 (or C23H25O12+ or C23H25ClO12, molar mass: 493.43 g/mol (528.89 g/mol for chloride), exact mass: 493.13460119 (528.103454 (for chloride)) may refer to:
The molecular formula C19H19NO4 (molar mass: 325.35 g/mol, exact mass: 325.131408 u) may refer to: