
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis. Grapes are a non-climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.

The pomegranate is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between 5 and 10 m tall.

Polyphenols are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments.
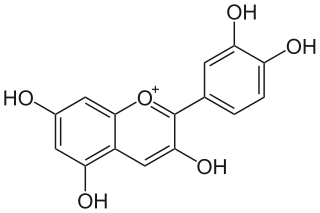
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin. It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH < 3, violet at pH 7-8, and blue at pH > 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator.

The health effects of wine are mainly determined by its active ingredient – alcohol. Preliminary studies found that drinking small quantities of wine, particularly of red wine, may be associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases, cognitive decline, stroke, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and early death. Other studies found no such effects.

A polyphenol antioxidant is a hypothetized type of antioxidant, in which each instance would contain a polyphenolic substructure; such instances which have been studied in vitro. Numbering over 4,000 distinct chemical structures, such polyphenols may have antioxidant activity {{{1}}} in vitro (although they are unlikely to be antioxidants in vivo). Hypothetically, they may affect cell-to-cell signaling, receptor sensitivity, inflammatory enzyme activity or gene regulation, although high-quality clinical research has not confirmed any of these possible effects in humans as of 2020.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

The color of wine is one of the most easily recognizable characteristics of wines. Color is also an element in wine tasting since heavy wines generally have a deeper color. The accessory traditionally used to judge the wine color was the tastevin, a shallow cup allowing one to see the color of the liquid in the dim light of a cellar. The color is an element in the classification of wines.
The pyranoanthocyanins are a type of pyranoflavonoids. They are chemical compounds formed in red wines by yeast during fermentation processes or during controlled oxygenation processes during the aging of wine. The different classes of pyranoanthocyanins are carboxypyranoanthocyanins, methylpyranoanthocyanins, pyranoanthocyanin-flavanols, pyranoanthocyanin-phenols, portisins, oxovitisins and pyranoanthocyanin dimers; their general structure includes an additional ring that may have different substituents linked directly at C-10.

Laricitrin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

Vitisin A is a natural phenol found in red wines. It is a pyranoanthocyanin.
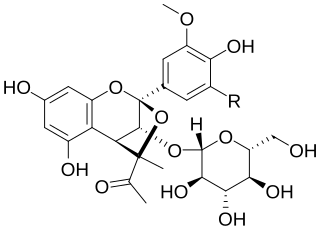
Castavinols are natural phenolic compounds found in red wines. These molecules are colorless and are derived from anthocyanin pigments. Thus their formation leads to a wine color loss.
4-Vinylphenol is an organic compound with the formula C2H3C6H4OH. It is the most studied of the three isomeric vinylphenols. It is a white volatile solid.

Malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin is a flavanol-anthocyanin adduct. Flavanol-anthocyanin adducts are formed during wine ageing through reactions between anthocyanins and tannins present in grape, with yeast metabolites such as acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde-induced reactions yield ethyl-linked species such as malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin.
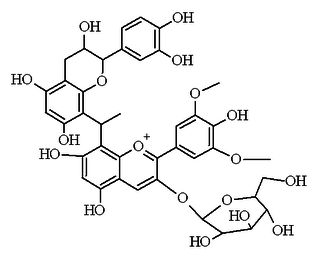
Flavanol-anthocyanin adducts are formed during wine ageing through reactions between anthocyanins and tannins present in grape, with yeast metabolites such as acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde-induced reactions yield ethyl-linked species such as malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin.

p-Coumaroylated anthocyanins are a type of anthocyanins with a p-coumaric acid unit linked with a sugar to an anthocyanidin aglycone. 3-(6-p-Coumaroyl)glucosides are found in grape and wine. Cyanidin-3-O-(di-p-coumarylglucoside)-5-glucoside is found in dark opal basil. Red leaves of Perilla frutescens also accumulate cyanidin 3-(6-O-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucoside)-5-(6-O-malonyl-β-D-glucoside).
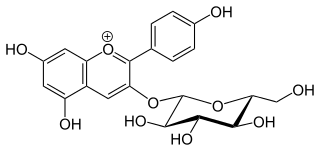
Callistephin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-O-glucoside of pelargonidin.

Cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside, also known as cyanin, is an anthocyanin. It is the 3,5-O-diglucoside of cyanidin.

















