
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis.

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of Vitis, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.

Delphinidin is an anthocyanidin, a primary plant pigment, and also an antioxidant. Delphinidin gives blue hues to flowers in the genera Viola and Delphinium. It also gives the blue-red color of the grape that produces Cabernet Sauvignon, and can be found in cranberries and Concord grapes as well as pomegranates, and bilberries.
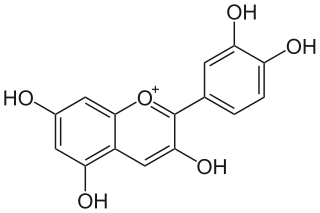
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin. It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH < 3, violet at pH 7-8, and blue at pH > 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. In a recent study, cyanidin was found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator.

Malvin is a naturally occurring chemical of the anthocyanin family.

Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, the 3',5'-methoxy derivative of delphinidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature.

Betalains are a class of red and yellow indole-derived pigments found in plants of the Caryophyllales, where they replace anthocyanin pigments. Betalains also occur in some higher order fungi. They are most often noticeable in the petals of flowers, but may color the fruits, leaves, stems, and roots of plants that contain them. They include pigments such as those found in beets.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Petunidin (Pt), like Europinidin and Malvidin, is derived from Delphinidin and is an O-methylated anthocyanidin of the 3-hydroxy type. It is a natural organic compound, a dark-red or purple water-soluble pigment found in many redberries including chokeberries, Saskatoon berries or different species of grape, and also part of the pigments responsible for the petal colors in many flowers. This pigment gives the Indigo Rose tomatoes the majority of their deep purple color when the fruits are exposed to sunlight. The name of the molecule itself is derived from the word Petunia.

The color of wine is one of the most easily recognizable characteristics of wines. Color is also an element in wine tasting since heavy wines generally have a deeper color. The accessory traditionally used to judge the wine color was the tastevin, a shallow cup allowing one to see the color of the liquid in the dim light of a cellar. The color is an element in the classification of wines.
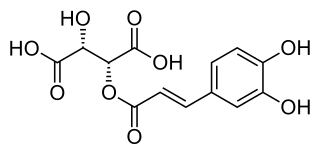
Caftaric acid is a non-flavanoid phenolic compound.

Oenin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of malvidin. It is one of the red pigments found in the skin of purple grapes and in wine.

Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.
The pyranoanthocyanins are a type of pyranoflavonoids. They are chemical compounds formed in red wines by yeast during fermentation processes or during controlled oxygenation processes during the aging of wine. The different classes of pyranoanthocyanins are carboxypyranoanthocyanins, methylpyranoanthocyanins, pyranoanthocyanin-flavanols, pyranoanthocyanin-phenols, portisins, oxovitisins and pyranoanthocyanin dimers; their general structure includes an additional ring that may have different substituents linked directly at C-10.
Copigmentation is a phenomenon where pigmentation due to anthocyanidins is reinforced by the presence of other colorless flavonoids known as cofactors or “copigments”. This occurs by the formation of a non-covalently-linked complex.

Vitisin A is a natural phenol found in red wines. It is a pyranoanthocyanin.
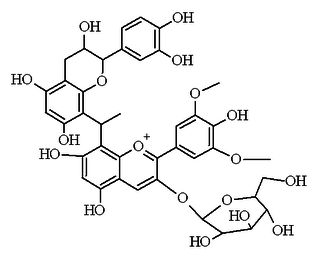
Malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin is a flavanol-anthocyanin adduct. Flavanol-anthocyanin adducts are formed during wine ageing through reactions between anthocyanins and tannins present in grape, with yeast metabolites such as acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde-induced reactions yield ethyl-linked species such as malvidin glucoside-ethyl-catechin.

Malvidin-3-O-(6-p-coumaroyl)glucoside is a p-coumaroylated anthocyanin found in grape and wine. There are two forms with the cis and trans isomers of p-coumaric acid. It is a cation.
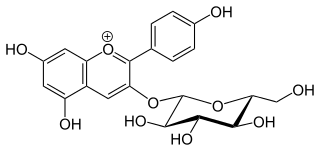
Callistephin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-O-glucoside of pelargonidin.



















