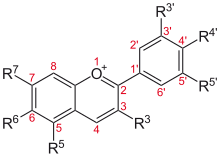
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.

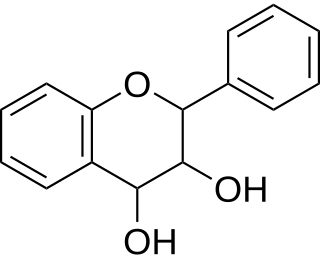
Flavan-3-ols are a subgroup of flavonoids. They are derivatives of flavans that possess a 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-ol skeleton. Flavan-3-ols are structurally diverse and include a range of compounds, such as catechin, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, proanthocyanidins, theaflavins, thearubigins. They play a part in plant defense and are present in the majority of plants.

Polyphenols are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments.

Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized de novo by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility.

Flavones are a class of flavonoids based on the backbone of 2-phenylchromen-4-one (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one).
In enzymology, a dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase (EC 1.1.1.219) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanidin reductase (EC 1.3.1.77) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucocyanidin oxygenase (EC 1.14.11.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.
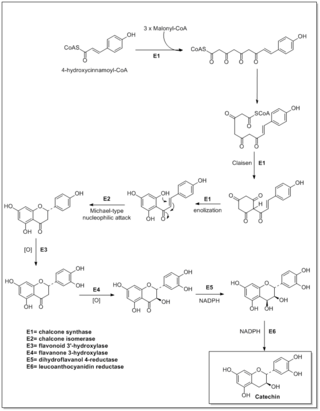
Flavonoids are synthesized by the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the amino acid phenylalanine is used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, many products can be formed, including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

Apigeninidin is a chemical compound belonging to the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and that can be found in the Patagonian plant Ephedra frustillata and in the soybean. Apigeninidin is one of the principal pigments found in sorghum. Extremely high level of apigeninidin (49 mg/g) has been documented in sorghum leaf sheath. Like all anthocyanidins it exists in a variety of tautomers depending on pH and hydration, several of these bare the distinctive pyrylium core.
Leucoanthocyanidin (flavan-3,4-diols) are colorless chemical compounds related to anthocyanidins and anthocyanins. Leucoanthocyanins can be found in Anadenanthera peregrina and in several species of Nepenthes including N. burbidgeae, N. muluensis, N. rajah, N. tentaculata, and N. × alisaputrana.

The flavan-4-ols (3-deoxyflavonoids) are flavone-derived alcohols and a family of flavonoids. Flavan-4-ols are colorless precursor compounds that polymerize to form red phlobaphene pigments. They can be found in the sorghum. Glycosides can be isolated from a methanol extract of the rhizomes of Abacopteris penangiana.

Phlobaphenes are reddish, alcohol-soluble and water-insoluble phenolic substances. They can be extracted from plants, or be the result from treatment of tannin extracts with mineral acids. The name phlobaphen come from the Greek roots φλoιὀς (phloios) meaning bark and βαφή (baphe) meaning dye.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.
Tyrosine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.41, tyrosine N-hydroxylase, CYP79A1) is an enzyme with systematic name L-tyrosine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Pisatin (3-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4′,5′-methylenedioxy-chromanocoumarane) is the major phytoalexin made by the pea plant Pisum sativum. It was the first phytoalexin to be purified and chemically identified. The molecular formula is C17H14O6.