
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ensembles, which can be used to predict metabolite abundances in biological samples from, for example mRNA abundances. One of the ultimate challenges of systems biology is to integrate metabolomics with all other -omics information to provide a better understanding of cellular biology.
The molecular formula C21H20O11 (molar mass: 448.38 g/mol, exact mass: 448.100561 u) may refer to:

Vitexin is an apigenin flavone glucoside, a chemical compound found in the passion flower, Vitex agnus-castus, in the Phyllostachys nigra bamboo leaves, in the pearl millet, and in Hawthorn.
The molecular formula C21H20O10 (molar mass: 432.38 g/mol, exact mass: 432.105647 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C16H13O7 (or C16H13O7+, molar mass : 317.27 g/mol, exact mass : 317.066127317) or C16H13ClO7 (exact mass : 352.03498) may refer to:

The flavanonols are a class of flavonoids that use the 3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone.
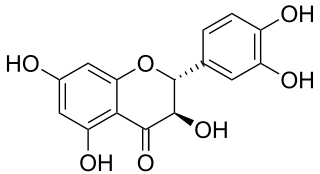
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols.
The molecular formula C21H21O11+ (molar mass: 449.38 g/mol, exact mass: 449.108386 u) may refer to:

Azaleatin is a chemical compound. It is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It was first isolated from the flowers of Rhododendron mucronatum in 1956 and has since been recorded in forty-four other Rhododendron species, in Plumbago capensis, in Ceratostigma willmottiana and in Carya pecan. It has been also been found in the leaves of Eucryphia.
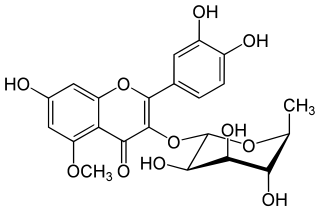
Azalein is a chemical compound. It is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is the 3-O-α-L-rhamnoside of azaleatin. It can be found in the flowers of Plumbago and Rhododendron species.
The molecular formula C22H23O11, molarMass = 463.41 g/mol (Aglycone), exact mass : 463.124036578 u (C22H23O11+ (aglycone), C22H23O11Cl (chloride), 498.9 g/mol (chloride)) may refer to:
The molecular formula C22H23O12, molar mass: 479.41 g/mol (aglycone), 514.86 g/mol (chloride), exact mass : 479.1189512 u (C22H23O12+ (aglycone), C22H23O12Cl (chloride)) may refer to:

An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound, which is a type of flavonoid. There are two isomers of the molecule, with (E)- and (Z)-configurations. The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2. In aurone, a chalcone-like group is closed into a 5-membered ring instead of the 6-membered ring more typical of flavonoids.
The molecular formula C21H24O11 (molar mass: 452.41 g/mol, exact mass: 452.131862 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C23H24O12 (exact mass: 492.12677623) may refer to:

Marein is a chalconoid, a type of natural phenol. It is the 4'-O-glucoside of okanin. It can be found in Coreopsis maritima. It is an anthochlor pigment, a kind of yellow pigment.

Syringetin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape, in Lysimachia congestiflora and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.
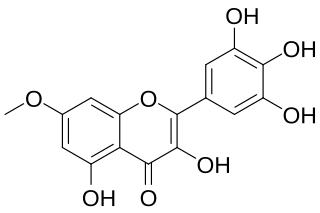
Europetin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in Plumbago europaea and it can be prepared synthetically.
Plumbago pulchella is a species of flowering plant on the Plumbaginaceae family. It is referred to by the common name cola de iguana.

Echinops echinatus, the Indian globe thistle, commonly known as Usnakantaka, is a species of globe thistle, found in India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Indian globe thistle is an erect branched herb about 100 cm high. It has short, stout stems, branching from the base, covered with white cottony hair. Alternately arranged oblong, deeply pinnatifid leaves are 7–12 cm long. Flower heads occur in solitary white spherical balls, 3–5 cm across. Petals of the tiny white disc florets are 5 mm long. Flowers are surrounded by straight, strong, white bristles. Often misidentified with Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertner, it is colloquially known as Camel's thistle.











