C2H4O2 may refer to:
Compounds sharing the molecular formula:
- Acetic acid
- Dihydroxyethene isomers:
- 1,1-Dihydroxyethene
- (E)-1,2-Dihydroxyethene
- (Z)-1,2-Dihydroxyethene
- Dioxetane isomers:
- Glycolaldehyde
- Methyldioxirane
- Methyl formate
- Oxiranol
C2H4O2 may refer to:
Compounds sharing the molecular formula:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.

In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer.
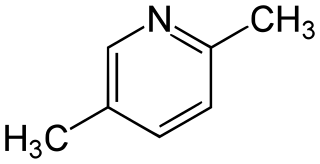
Lutidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are dimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Lutidine comes in several isomers:
Dichloroethene or dichloroethylene, often abbreviated as DCE, can refer to any one of several isomeric forms of the organochloride with the molecular formula C2H2Cl2:

Dimethoxybenzene is a group of organic compounds which are dimethoxy derivatives of benzene. Dimethoxybenzene comes in three isomers:
1,3-Dioxetane (1,3-dioxacyclobutane) is a heterocyclic organic compound with formula C2O2H4, whose backbone is a four-member ring of alternating oxygen and carbon atoms. It can be viewed as a dimer of formaldehyde (COH2).
The molecular formula C3H6O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H12O (molar mass: 88.15 g/mol, exact mass: 88.088815) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H12 may refer to following structural isomers:
A dioxetane or dioxacyclobutane is an organic compound with formula C2O2H4, whose backbone is a four-membered ring of two oxygen atoms and two carbon atoms. There are two isomers:
The molecular formula C2O4 may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H12 may refer to one of many molecules, including:

Tetrahydroxybenzenes or Benzenetetrols are a group of organic compounds which are tetrahydroxy derivatives of benzene. Tetrahydroxybenzene comes in three isomers:
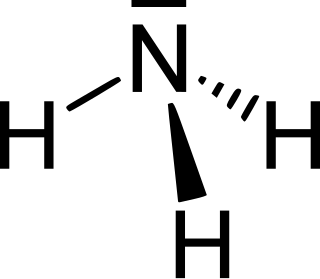
Azanes are acyclic, saturated hydronitrogens, which means that they consist only of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms and all bonds are single bonds. They are therefore pnictogen hydrides. Because cyclic hydronitrogens are excluded by definition, the azanes comprise a homologous series of inorganic compounds with the general chemical formula N
nH
n+2.
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
Nonynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C9H16.
Decynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C10H18.
The molecular formula C10H8O2 may refer to:
Heptynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C7H12.