This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent.

The Federal Analogue Act, 21 U.S.C. § 813, is a section of the United States Controlled Substances Act passed in 1986 which allowed any chemical "substantially similar" to a controlled substance listed in Schedule I or II to be treated as if it were also listed in those schedules, but only if intended for human consumption. These similar substances are often called designer drugs.
Acetoin, also known as 3-hydroxybutanone or acetyl methyl carbinol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)C(O)CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant, buttery odor. It is chiral. The form produced by bacteria is (R)-acetoin.
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)4NH. It is a cyclic secondary amine, also classified as a saturated heterocycle. It is a colourless liquid that is miscible with water and most organic solvents. It has a characteristic odor that has been described as "ammoniacal, fishy, shellfish-like". In addition to pyrrolidine itself, many substituted pyrrolidines are known.
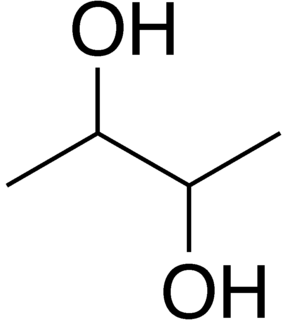
2,3-Butanediol fermentation is anaerobic fermentation of glucose with 2,3-butanediol as one of the end products. The overall stoichiometry of the reaction is

1,4-Butynediol is an organic compound that is an alkyne and a diol. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a commercially significant compound in its own right and as a precursor to other products.
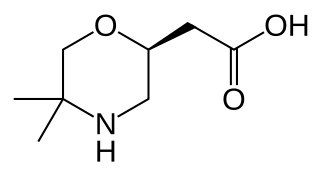
SCH-50911 is a selective GABAB antagonist. Its main applications are in pharmacology research.
PBAT is a biodegradable random copolymer, specifically a copolyester of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid. PBAT is produced by many different manufacturers and may be known by the brand names ecoflex®, Wango, Ecoworld, Eastar Bio, and Origo-Bi. It is also called poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and sometimes polybutyrate-adipate-terephthalate or even just "polybutyrate". It is generally marketed as a fully biodegradable alternative to low-density polyethylene, having many similar properties including flexibility and resilience, allowing it to be used for many similar uses such as plastic bags and wraps. The structure of the PBAT polymer is shown to the right. It is depicted as a block co-polymer here due to the common synthetic method of first synthesizing two copolymer blocks and then combining them. However, it is important to note that the actual structure of the polymer is a random co-polymer of the blocks shown.

In enzymology, a (R,R)-butanediol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S,S)-butanediol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.76) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
1,5-Pentanediol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH. Like other diols, this viscous colourless liquid is used as plasticizer and also forms polyesters that are used as emulsifying agents and resin intermediates.

Aceburic acid (INN), also known as 4-acetoxybutanoic acid or 4-hydroxybutyric acid acetate, is drug described as an analgesic which was never marketed. It is the acetyl ester of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, and based on its structural relation to GHB, is likely to behave as a prodrug to it.
Diacetyl reductase ((R)-acetoin forming) (EC 1.1.1.303, (R)-acetoin dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (R)-acetoin:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Diacetyl reductase ((S)-acetoin forming) (EC 1.1.1.304, (S)-acetoin dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (S)-acetoin:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
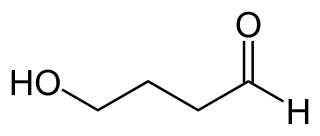
γ-Hydroxybutyraldehyde, also referred to as GHBAL, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde or γ-hydroxybutanal, is a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) from 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD). Like 1,4-BD, it also behaves as a prodrug to GHB when taken exogenously. However, as with all aliphatic aldehydes, γ-hydroxybutaldehyde is caustic and is strong-smelling and foul-tasting; thus, actual ingestion of this compound is likely to be unpleasant and result in severe nausea and vomiting.