The molecular formula C6H7N (molar mass: 93.12 g/mol, exact mass: 93.0578 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H7N (molar mass: 93.12 g/mol, exact mass: 93.0578 u) may refer to:
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
The molecular formula C21H23NO5 (molar mass: 369.41 g/mol, exact mass: 369.1576 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H8O7 (molar mass: 192.12 g/mol, exact mass: 192.0270 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula BaSO4 (molar mass: 233.39 g/mol, exact mass: 233.8570 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.07825 u) may refer to:
The Chichibabin pyridine synthesis is a method for synthesizing pyridine rings. The reaction involves the condensation reaction of aldehydes, ketones, α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds, or any combination of the above, with ammonia. It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin in 1924. Methyl-substituted pyridines, which show widespread uses among multiple fields of applied chemistry, are prepared by this methodology.
The molecular formula C6H10O7 (molar mass: 194.14 g/mol, exact mass: 194.0427 u) may refer to:
2-Methylpyridine, or 2-picoline, is the compound described with formula C6H7N. 2-Picoline is a colorless liquid that has an unpleasant odor similar to pyridine. It is mainly used to make vinylpyridine and the agrichemical nitrapyrin.
4-Methylpyridine is the organic compound with the formula CH3C5H4N. It is one of the three isomers of methylpyridine. This pungent liquid is a building block for the synthesis of other heterocyclic compounds. Its conjugate acid, the 4-methylpyridinium ion, has a pKa of 5.98, about 0.7 units above that of pyridine itself.
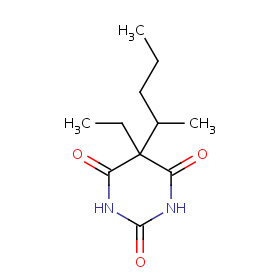
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C14H12O3 (molar mass: 228.25 g/mol, exact mass: 228.078644 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2HCl2F3 (molar mass: 152.93 g/mol, exact mass: 151.9407 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6S2 (molar mass: 94.20 g/mol, exact mass: 93.99109 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C8H16 (molar mass: 112.21 g/mol, exact mass: 112.1252 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H11O6 (C15H11O6+, molar mass: 287.24 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0555626 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H11O7 (molar mass: 303.24 g/mol, exact mass: 303.050477 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H25N3O (molar mass: 263.38 g/mol, exact mass: 263.1998 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H18BrNO2 (molar mass: 288.18 g/mol, exact mass: 287.0521 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C17H23N5O2 (molar mass: 329.40 g/mol, exact mass: 329.1852 u) may refer to: