The molecular formula C7H16O may refer to:
The molecular formula C7H16O may refer to:
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
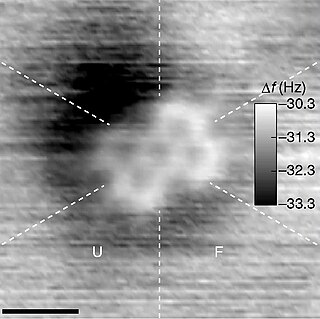
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
Benzol may refer to:

In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a chemical formula. The informal use of the term formula in science refers to the general construct of a relationship between given quantities.

The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. Unlike other chemical formula types, which have a limited number of symbols and are capable of only limited descriptive power, structural formulas provide a more complete geometric representation of the molecular structure. For example, many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different enantiomeric structures but the same molecular formula. There are multiple types of ways to draw these structural formulas such as: Lewis Structures, condensed formulas, skeletal formulas, Newman projections, Cyclohexane conformations, Haworth projections, and Fischer projections.

1-Heptanol is an alcohol with a seven carbon chain and the structural formula of CH3(CH2)6OH. It is a clear colorless liquid that is very slightly soluble in water, but miscible with ether and ethanol.

Casomorphin is an opioid peptide derived from the digestion of the milk protein casein.

1-Hexene (hex-1-ene) is an organic compound with the formula C6H12. It is an alkene that is classified in industry as higher olefin and an alpha-olefin, the latter term meaning that the double bond is located at the alpha (primary) position, endowing the compound with higher reactivity and thus useful chemical properties. 1-Hexene is an industrially significant linear alpha olefin. 1-Hexene is a colourless liquid.
Heptanol may refer to any isomeric alcohols with the formula C7H16O:
The molecular formula C6H12O may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H14 (molar mass: 86.17 g/mol) may refer to:
Dioxin may refer to:

2-Heptanol is a chemical compound which is an isomer of heptanol. It is a secondary alcohol with the hydroxyl on the second carbon of the straight seven-carbon chain.
The molecular formula C10H15N (molar mass: 149.23 g/mol, exact mass: 149.1204 u) may refer to:

3-Heptanol or heptan-3-ol is an organic alcohol with the chemical formula C7H16O.

4-Heptanone or heptan-4-one is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2CH2)2CO. It is a colorless liquid.
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
Nonynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C9H16.
Decynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C10H18.
Heptynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C7H12.