The molecular formula C9H6O3 (molar mass: 162.14 g/mol, exact mass: 162.031694 u) may refer to:
- Umbelliferone, also known as 7-hydroxycoumarin or hydrangine
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin
The molecular formula C9H6O3 (molar mass: 162.14 g/mol, exact mass: 162.031694 u) may refer to:
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
The molecular formula C2H2 (molar mass: 26.04 g/mol, exact mass: 26.01565 u) may refer to:
Gluten exorphins are a group of opioid peptides formed during digestion of the gluten protein. It has been hypothesized that people with autism and schizophrenia have abnormal leakage from the gut of these compounds, which then pass into the brain and disrupt brain function, a process collectively known as the opioid excess theory or a part of leaky gut syndrome. This is partly the basis for the gluten-free, casein-free diet. The medical evidence is mixed. Two clinical studies of autism patients who followed this diet found no benefit. Another study found a benefit. Another study suggested the diet may present a greater risk to brain development.
The molecular formula C6H8O7 (molar mass: 192.12 g/mol, exact mass: 192.0270 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula BaSO4 (molar mass: 233.39 g/mol, exact mass: 233.8570 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C2H6O (molar mass: 46.07 g/mol, exact mass: 46.04186 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10 (molar mass: 58.12 g/mol, exact mass: 58.07825 u) may refer to:

4-Hydroxycoumarins belong to a class of vitamin K antagonist (VKA) anticoagulant drug molecules derived from coumarin by adding a hydroxy group at the 4 position to obtain 4-hydroxycoumarin, then adding a large aromatic substituent at the 3-position. The large 3-position substituent is required for anticoagulant activity.
To see a more detailed description of these isomers, see Amyl alcohol.
The molecular formula C6H10O7 (molar mass: 194.14 g/mol, exact mass: 194.0427 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H10N2O2S (molar mass: 162.21 g/mol, exact mass: 162.0463 u) may refer to:
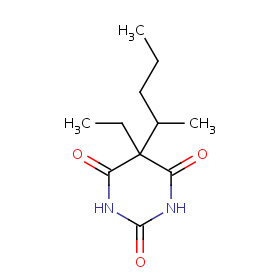
The molecular formula C11H18N2O3 (molar mass: 226.27 g/mol) may be referred as:
The molecular formula C8H16 (molar mass: 112.21 g/mol, exact mass: 112.1252 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C12H18 (molar mass: 162.27 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C10H10O2 (molar mass : 162.18 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C10H7Cl (molar mass: 162.62 g/mol, exact mass: 162.0236 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C9H10N2O (molar mass: 162.19 g/mol, exact mass: 162.0793 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C8H18O3 (molar mass: 162.229 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H10O5, of molecular weight 162.14, may refer to: