
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery.

Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA. It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 172 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the major histocompatibility complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 193 million base pairs and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 150 million base pairs of nucleic acids and represents between 4.0 and 4.5% of the total DNA in cells.

Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UTRN gene. The name is a short form for ubiquitous dystrophin.

Spectrin beta chain, brain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTBN1 gene.

Centrosomal protein of 290 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP290 gene. CEP290 is located on the Q arm of chromosome 12.

Sperm flagellar protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPEF1 gene.

Leucine-rich repeat and calponin homology domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRCH4 gene.

Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 298 is a protein encoded by CFAP298 gene. It is of interest in part for its association with various diseases. It has been found in high levels in the bone marrow of patients with a negative prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia and an abnormal karyotype. Male Alzheimer's patients have shown a decrease in expression of CFAP298 in their blood cells. The CFAP298 gene lies within the critical region of Down Syndrome. There are no clear paralogs in humans, but the gene has homologues widely conserved among animals, fungi, and algae.
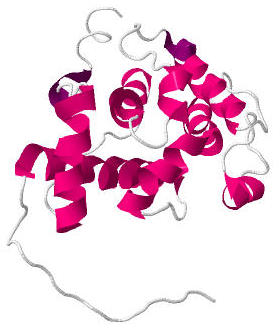
Calponin homology domain (or CH domain) is a family of actin binding domains found in both cytoskeletal proteins and signal transduction proteins. The domain is about 100 amino acids in length and is composed of four alpha helices. It comprises the following groups of actin-binding domains:

Calponin 1 is a basic smooth muscle protein that in humans is encoded by the CNN1 gene.
Coiled-coil domain containing protein 180 (CCDC180) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC180 gene. This protein is known to localize to the nucleus and is thought to be involved in regulation of transcription as are many proteins containing coiled-coil domains. As it is expressed most highly in the testes and is regulated by SRY and SOX transcription factors, it could be involved in sex determination.

Cilia and flagella associated protein 157 (CFAP157) also known as chromosome 9 open reading frame 117 (c9orf117) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFAP157 gene.

Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 299 (CFAP299), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFAP299 gene. CFAP299 is predicted to play a role in spermatogenesis and cell apoptosis.

C20orf202 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C20orf202 gene. In humans, this gene encodes for a nuclear protein that is primarily expressed in the lung and placenta.

Chromosome 5 Open Reading Frame 47, or C5ORF47, is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the C5ORF47 gene. It also goes by the alias LOC133491. The human C5ORF47 gene is primarily expressed in the testis.

















